演算法筆記-排序
Selection Sort
The Champion Problem
給定一個陣列,求出陣列中最小數字的下標。
Input: an array A of n integers.
Output: an index k so that A[k] is the minimum value in A.
Code:
1 | int champion(int *s, int n){ |
Sort
給定一個陣列,將其排序為遞增的陣列。
Input: an array A of n integers.
Output: the same array with the n integers ordered nondecrementally.
Code:
1 | void selection_sort(int *s, int n){ |
利用 champion 找出剩餘陣列中最小數字的下標,將其放到對應的位置。
Insertion Sort
Insert a number into a sorted array
將一個整數 x 插入一個已排序陣列 A 中,並且保持 A 是排序的狀態。
Input: a sorted array A of n integers and an integer x.
Output: a sorted array that comprises all elements in A and x.
Code:
1 | void insert(int *s, int n, int x){ |
由後向前檢查合適的插入位置,如果到最後還沒有找到,則置於 s[0]。
Sort
給定一個陣列,將其排序為遞增的陣列。
Input: an array A of n integers.
Output: the same array with the n integers ordered nondecrementally.
Code:
1 | void insertion_sort(int *s, int n){ |
由 s[1] 開始,依序將數字插入其前方已排序的陣列中。
Merge Sort
Merge two sorted arrays
將兩個已排序的陣列 A 和 B 合併為一個排序的陣列。
Input: two sorted arrays A and B of integers.
Output: a sorted array that comprises all elements in A and B.
Code:
1 | int* merge(int *s, int n, int *r, int m){ |
Sort
給定一個陣列,將其排序為遞增的陣列。
Input: an array A of n integers.
Output: the same array with the n integers ordered nondecrementally.
Code:
1 | void merge_sort(int *s, int n){ |
利用遞迴的方式不斷將陣列分為兩部分進行排序,之後進行合併。
2D Sorted Arrays - Young Tableau
這裡要介紹的不是排序演算法,而是一個資料結構 Young Tableau (楊表),Young Tableau 是一個 m * n 的矩陣,其特性是矩陣的每一行與列都是以遞增排序的 (由上而下、由左至右),並且能在 O(m + n) 的時間複雜度下進行插入及查詢資料。
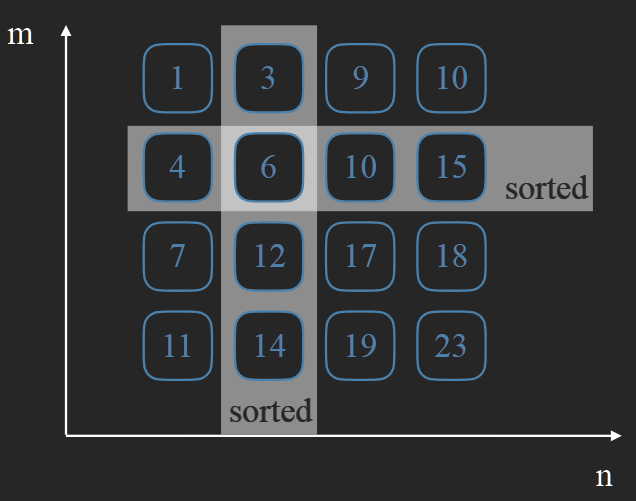
查詢
由二維陣列的右上角開始進行比對,每次與目標數字 x 比較有三種結果:
- 大於
x:將比對的格子向左移動,如果無法左移則結束。 - 等於
x:找到目標,結束。 - 小於
x:將比對的格子向下移動,如果無法下移則結束。
插入
將要插入的數字先放在二維陣列的右下角,檢查是否滿足 Young Tableau,如果不滿足則進行比較,每次比較其上方的數字 T 與左方的數字 L,如果該位置為空白則代表無限,比較有兩種結果:
L >= T:將插入的數字與L交換。L < T:將插入的數字與T交換。
當滿足Young Tableau或是數字到達頂端或最左方時結束。
Heap Sort
Max-Heapify
調整指定的根結點與左右子結點,並且向下遞迴,使根結點為最大。
Max-Heapify(A, i)
convert the subtree rooted at node i into a max heap assuming that
(1) the subtree rooted at node Left(i) is a max heap, and
(2) the subtree rooted at node Right(i) is a max heap.
Build-Max-Heap
使指定的子樹滿足 Max Heap。
Convert the subtree rooted at node i into a max heap without the
assumption that heapification uses.
Code:
1 | Build-Max-Heap(A, i){ |
Extract-Max
取出 Max Heap 裡面的最大值。
Extract-Max(A, n)
Remove the maximum from an n-element array A and keep the rest of A
as a max heap.
Code:
1 | Extract-Max(A, int& n){ |
Sort
給定一個陣列,將其排序為遞增的陣列。
Input: an array A of n integers.
Output: the same array with the n integers ordered nondecrementally.
Code:
1 | HeapSort(A, n){ |
不斷從 Max Heap 中取出最大值構成新的陣列。
Quick Sort
使用分治的方式進行排序,在陣列中選擇一個 pivot,並將陣列分成 小於等於 pivot 以及 大於 pivot 兩個部分,再以遞迴的方式接著處理兩個陣列,直到排序結束。
Sort
使用了長度為 n 的額外空間。
Code:
1 | void QuickSort(int *A, int n, int *buf){ |
In-Place Sort
不使用額外空間。
Code:
1 | void QuickSort(int *A, int n){ |
Counting Sort
根據資料的範圍,建立 k 個 bucket (通常是先進先出的容器),遍歷整個陣列
並將各個元素分配到對應的 bucket 中,之後將各個 bucket 串起來就完成排序了,通常 k 的值不能太大。
Radix Sort
通常用於數字較大的排序 (可以比 Counting Sort 省空間) 或是將字串按照字典序進行排序,原理主要是利用 Counting Sort 對數字的各個位數 (或是字串的各個元素) 進行操作。
base 10
由最低位數 (最右邊的數字) 開始,對該位數進行 Counting Sort,形成新的陣列,接著對第二低的位數排序,如果元素的長度不夠可以補 0,重複直到所有元素的最高位數,最後型的的陣列就是已排序的結果。
base 100 (優化)
與 base 10 的操作類似,不過一次是對兩個位數進行操作,每次建立 100 個 bucket 進行排序,可以減少操作的次數。





