發展心理學筆記-L9
L9 Moving into the Adult Social World: Socioemotional Development in Adolescence
Identity and Self-Esteem
The Search for Identity
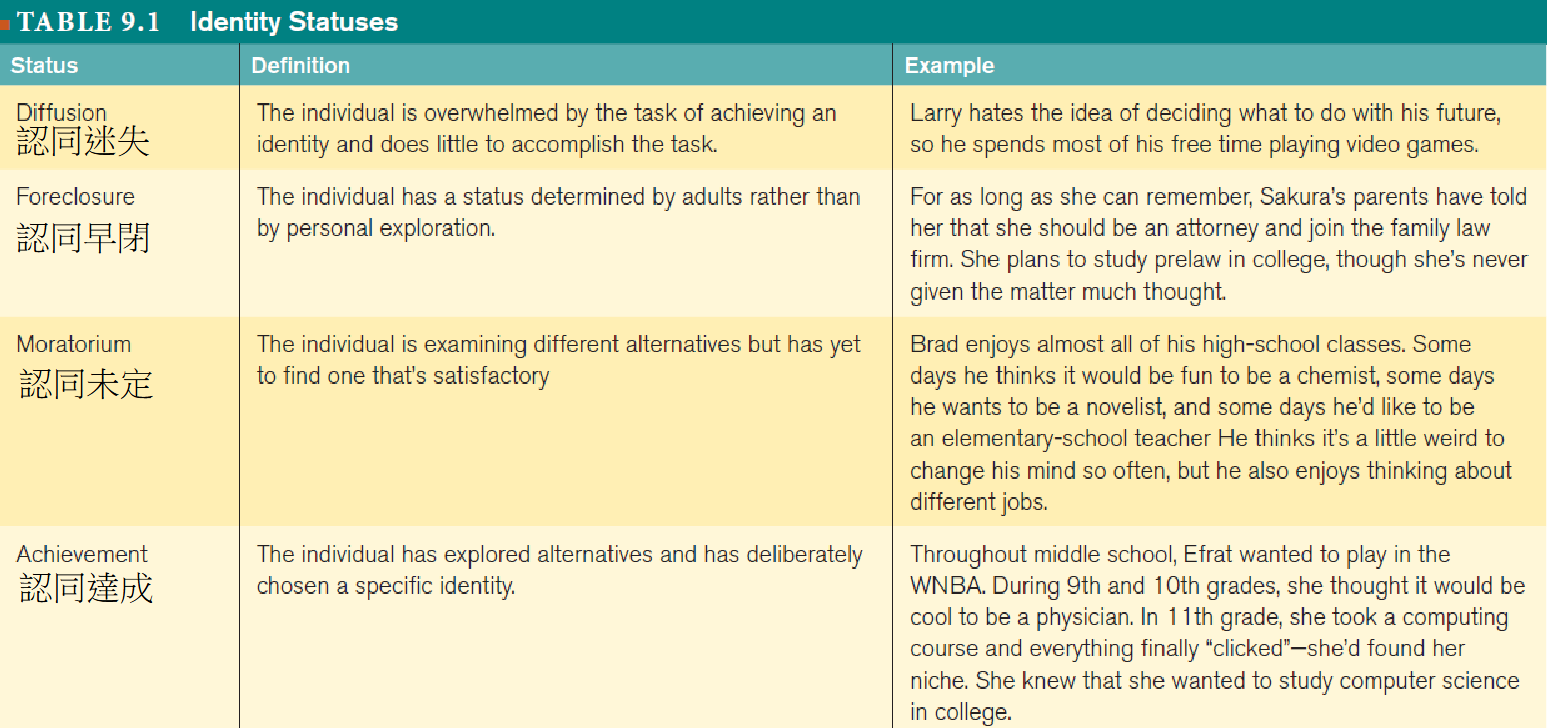
| 有尋找認同 | 無尋找認同 | |
|---|---|---|
| 找到認同 | 認同達成 | 認同早閉 |
| 沒有找到認同 | 認同未定 | 認同迷失 |
Characteristic ways of thinking during identity search
Adolescent egocentrism 青少年自我中心- 只專注於自己的感覺與經歷- imaginary audience 想像觀眾 - 相信同伴一直在看著他們
- Personal fable 個人神話寓言 - 相信他們自己的經歷和感受是獨一無二的
- Illusion of invulnerability 無懈可擊的錯覺 - 相信不幸只會發生在別人身上
- 找到認同之後,這些自我中心的想法會逐漸消失
Who/What helps teens form identities?
- Parents - 開放討論並允許孩子探索不同的選擇
- Peers - 親密、值得信賴的朋友
- Broader social context - 貧困的侷限性
- Personality - 對經驗的開放性
Ethnic Identity 種族認同
Typically three phases in achieving an ethnic identity:
- Initially, no examination of ethnic roots
- Explore the personal impact of one’s cultural heritage
- Achieve a distinct ethnic self-concept
Benefits of a strong ethnic identity:
- 更高的自尊心
- 與家人和朋友更愉快的互動
- 在學校的表現更好
Romantic Relationships and Sexuality
Romantic Relationships
- 以友情為基礎建立
- 發生在受歡迎程度和物理吸引力類似的人之間
- 隨著青少年的發展,信任和同情在人際關係中變得越來越重要
- 關係之中的青少年通常會
更有自信 - 可能會有更多的情感衝突
Sexual Behavior
- 男女差異
- 男生 - 更多視為娛樂
- 女生 - 更多視為愛與浪漫的表達
- Teen Pregnancy
- 美國未成年懷孕率比台灣高
- 沒有使用避孕方法
- 使用無效的避孕方法
- 降低未成年懷孕數量
- 完善的性教育
- 美國未成年懷孕率比台灣高
Sexual Orientation
- Approx. 15% of teens question their sexual and emotional attraction at some period
- Approx. 5% end up identifying as gay or lesbian
- 男生通常比女生早發現自己是同性戀者
- 同性戀者在青年時期可能會有心理健康問題
Dating Violence
- Approx. 25% of teens experience physical, emotional, and/or sexual violence while dating
- 可能造成學業或行為問題
- Risk factors:
- 父母行為、同伴行為
- 態度與個性
The World of Work
Career Development
經歷三個階段:
- Crystallization (13 - 14)
- teens use their emerging identities to form ideas about careers
- Specification (~18)
- learn more about specific lines of work and begin training
- Implementation
- enter workforce and learn first-hand from jobs
相關理論:
- Super’s theory -
自我認同(identity)是職業發展的主要推動力 (會隨時間改變)- does not explain why people are attracted to certain kinds of work
- Personality-type theory - 職業選擇是
人格的表現- 當一個人的人格特質和工作環境相同時,就會感到
滿足、成功且穩定 - by John Holland
-
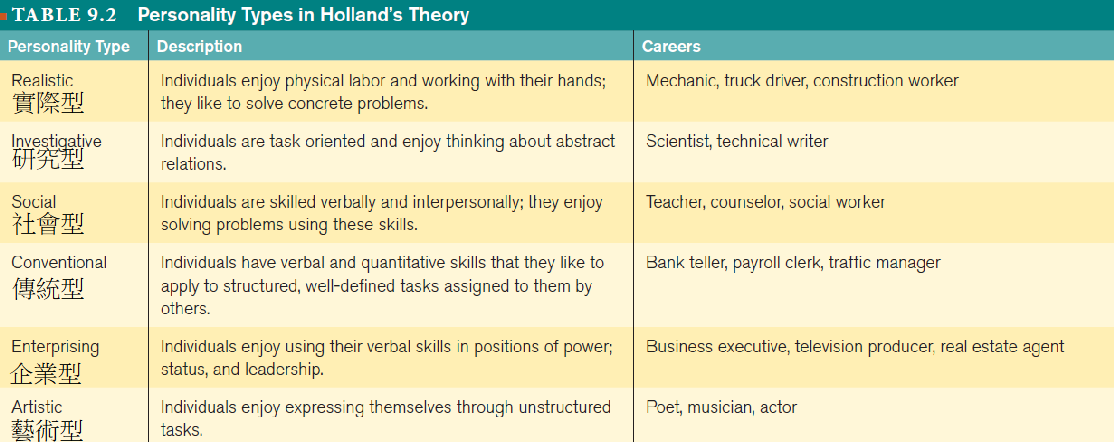
- 當一個人的人格特質和工作環境相同時,就會感到
Career Development Satisfaction
- Personalities
- Other factors:
- Pay
- workplace
stress - work-family balance
- etc.
Part-Time Employment
- 缺點:
- 長時間工作可能導致學業表現不佳
- 壓力過大的工作可能造成心理健康與行為問題
- 降低自尊心、焦慮
- Misleading affluence (誤導性的富裕)
- 把打工賺到的錢花在自己身上 (娛樂、奢侈品…)
The Dark Side
Alcohol
- 大多數美國青少年都承認使用酒精
- 受父母影響
- 生活壓力
- 受同儕影響
Smoking cigarettes
- 容易受到同儕影響
- School-based programs
- 教導抽菸會造成的影響
- 教導如何拒絕同儕的壓力
Depression
- 表徵:
- 悲傷
- 易怒
- 低自尊
- 約15%的青少年,且女生較多
- 原因通常是因為重大的損失或失敗
- ex: death of a family member or a terrible date
Why do only some teens become depression
- Temperament
- 調節情緒困難的人更容易抑鬱
- A belief system
internalizes failure 失敗內部化- 將失敗認為是自己的特質
- Family
- 情感疏離的父母
- 過度懲罰的父母
- 家庭壓力大
- Heredity 遺傳
- 神經傳導物質水平較低
Depression Treatment
- Antidepressant drugs 抗抑鬱藥
- 僅適用於某些青少年 (不是永久解決方案)
- Psychotherapy 心理治療
- 對青少年來說較好
- 強調認知與社交技能
如果沒有得到妥善的治療可能導致:
- 學業表現不佳
- 人際關係困難
- 成年後的抑鬱症
Delinquency 犯罪
- 分類
- Adolescent-limited antisocial behavior 青少年反社會行為
- 行為通常比較輕微
- Life-course persistent antisocial behavior 終生反社會行為
- 從年紀較小時開始,並持續一生
- 5% 的青少年
- 大部分青少年犯罪問題的原因
- Adolescent-limited antisocial behavior 青少年反社會行為
- 原因
- 遺傳 - 天生攻擊性較高
- 認知技能
- 將別人的行為認為是有敵意的
- 衝動
- 家庭教養 - 過度包容 or 嚴厲
- 貧困





