通訊原理筆記-L8
L8 Traffic Channel Allocation
Channel Allocation
將頻譜 (radio spectrum) 分割成多個互不重疊的通道 (channels),讓使用者可以同時使用,並且盡可能地減少干擾
- Static vs. Dynamic
Static- 每個 cell 被分配了一組固定的頻道數量- equal: 每個 cell 分配相同數量
- non-uniform: 每個 cell 根據需求分配數量
Dynamic- 根據需求,動態分配頻道給需要的 cell
- 分類:
- Fixed Channel Allocation schemes (FCA schemes)
- Dynamic Channel Allocation schemes (DCA schemes)
- Hybrid Channel Allocation schemes (HCA schemes)
FCA
A set of channels is permanently allocated to each cell
- 因為 traffic 的短期波動 (使用者數量改變),導致服務品質下降、容量不足
- 解決方法:
Non-uniform Channel AllocationStatic Borrowing
Non-uniform Channel Allocation
- 提前知道每個 cell 的預期流量
Non-uniform compact pattern allocation- 目標: 最小化 system blocking probability
- Allocation pattern: 重複出現的配置,包含 allocated cell + co-channel cells (同頻 cell)
- Compact allocation pattern: pattern 使得每個 cell 的距離較短,緊密但又不會互相干擾
Static Borrowing
將低負載的 cell 的頻道重新分配給高負載 cell (distances ≥ the minimum reuse distance)
- Simple borrowing schemes
- Acceptor cell vs. Donor cell: 接收 vs. 提供
- 從哪裡借頻道:
- Borrowing from the richest: 從鄰近擁有最多空閒頻道的 cell 借
- Borrow-first-available: 按照預先定義好的順序檢查,遇到第一個可借頻道就借
- Basic algorithm with reassignment:
- 當自己原本的頻道 (nominal channel) 空閒,立刻歸還借用的頻道
- 優缺點:
- (+) 減少 call blocking
- (-) 造成
Channel locking: 避免干擾 - (-) 借走頻道後,可能導致
co-channel sets無法使用這些頻道 (可能產生干擾)
- Complex borrowing schemes
- Simple hybrid channel borrowing strategy
- 將頻道分為
Permanent、Reserved - Permanent for local calls
- Reserved can be lent to neighboring cells
- 將頻道分為
- Borrowing with channel ordering (BCO)
- 將頻道進行
優先級排序 - Local calls: 使用高優先級的頻道
- Channel borrowing: 從低優先級的頻道開始借
- 將頻道進行
- Borrowing with directional channel locking
- 只鎖定受影響的
扇區 (sectors)
- 只鎖定受影響的
- Simple hybrid channel borrowing strategy
DCA
Utilizing a central channel pool: 需要頻道時從中申請使用
- 從頻道池中選擇一個頻道給 cell,考慮 Cost Function:
- 鄰近小區的未來的 blocking probability
- Reuse distance
- 頻道的使用頻率
- 整體系統的 blocking probability
- 即時頻道佔用分布 (Instantaneous channel occupancy)
- 分類:
- Centralized - BS 之間不需要交流
- Distributed - BS 之間互相交流資訊
Centralized DCA schemes
FA(First available) - 選出第一個滿足 reuse distance 的可用頻道LODA(Locally optimized dynamic assignment) - 使用 Cost Function- base on the future blocking probability in the neighboring cells
RING(Selection with maximum usage on the reuse ring) - 在co-channel set中選擇使用頻率最高的頻道
Distributed DCA schemes
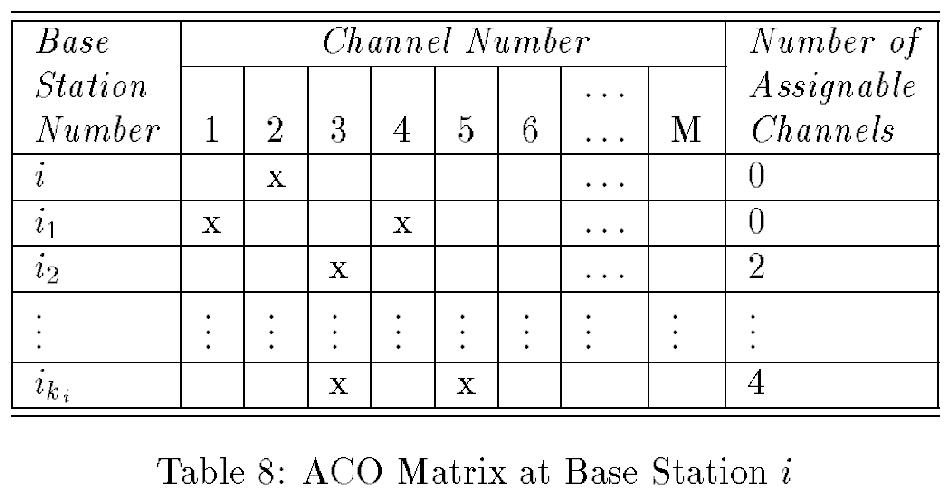
Cell-based: 每個 BS 自主決定要分配哪個頻道,並且隨時記錄附近頻道使用情況LP-DDCA(Local packing dynamic distributed channel assignment)ACO(Augmented channel occupancy) matrix- 紀錄頻道使用狀態
ACI(Adjacent channel interference constraint): LP-DDCA + ACI- ACO 中正在使用的頻道左右幾格應該保持空白,避免
Adjacent channel interference
- ACO 中正在使用的頻道左右幾格應該保持空白,避免
Signal strength measurement-based: 由 MS 和 BS 估算CIR(carrier-to-interference ratio),如果高於門檻則分配該頻道- SCS (Sequential channel search)
- 所有 BS/MS 都以相同的順序測試頻道,使用第一個滿足門檻的頻道
Service Interrupt: 通話的 CIR 降到門檻以下,強制中斷Instability: 被中斷的通話會重新尋找可用頻道,建立新連線時可能對其他頻道產生干擾Block: 沒有頻道滿足 CIR 門檻,造成 Block
- SCS (Sequential channel search)
HCA
Fixed + DCA
- 頻道被分為
Fixed and Dynamic set- Fixed set: 每個 cell 的專屬頻道
- Dynamic set: 當 Fixed set 用完時,使用 DCA schemes 請求頻道
- Design issue: Fixed & Dynamic set 的比例
Flexible channel allocation scheme
- 頻道被分為
Fixed and Flexible channel sets- Fixed channel set: 處理低流量
- Flexible channel set: 根據流量進行分配
- 分配方式:
- Scheduled
- 測量流量變化 (traffic variation)
- 預測流量高峰
- Predictive
- 監測流量以及 blocking probability
- Scheduled
Channel assignment strategy
- Fixed assignment (FA) strategy
- 將頻道永久分配給每個 cell
- 如果頻道全部使用,則 Block
- Borrowing with channel ordering (BCO) strategy
- 將頻道進行
優先級排序 - Local calls: 使用高優先級的頻道
- Channel borrowing: 從低優先級的頻道開始借
- 借用頻道之後,
lockreuse distance 內的所有 co-channel cells,避免干擾
- 將頻道進行
- Borrowing with directional channel locking (BDCL) strategy
- 只鎖定受影響的
扇區 (sectors) - ex: 當 P cell 向 A1 借用頻道 x,而 A3 只需要 lock 3,4,5 方向的頻道
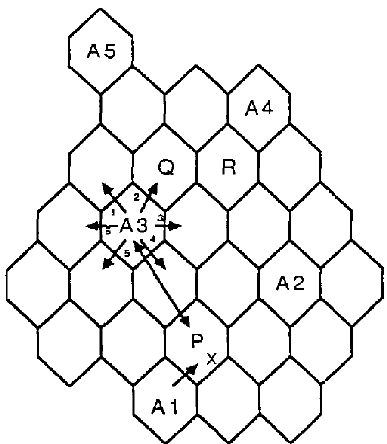
- 只鎖定受影響的
- Locally optimized dynamic assignment (LODA)
- No nominal channel is assigned to cells - 沒有專屬通道
- 要求頻道時,選擇 cost 最小的頻道
- cost: measure of the future call blocking probability
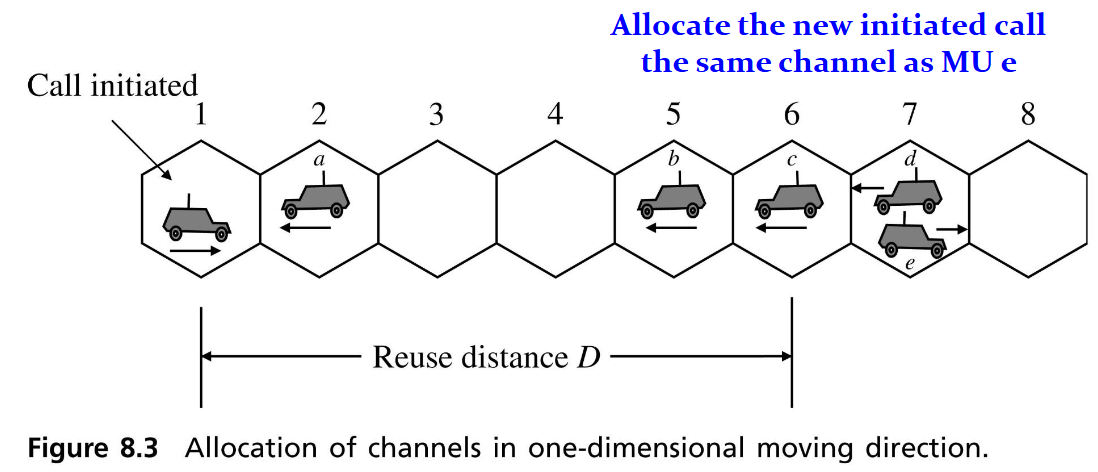
Channel Allocation in One-Dimensional Systems
Special case - 高速公路上
- 考慮標準:
- Reuse distance
- MS 移動方向
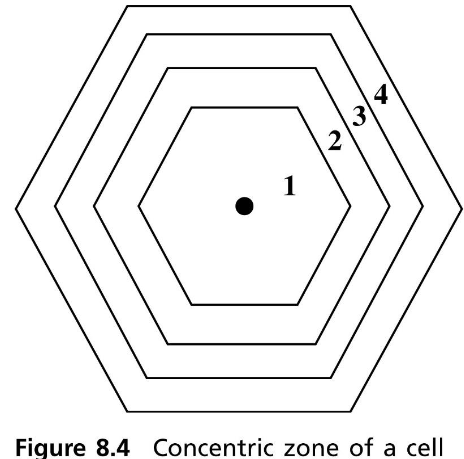
Reuse Partitioning-Based Channel Allocation
根據 power 分層
- 將 cell 分為
Inner zone vs. outer zone - 控制功率大小,較小的功率 -> 較低的 reuse distance
- 定期測量
SIR(Signal-to-Interference Ratio) - 根據 SIR 進行 Channel group adjustment
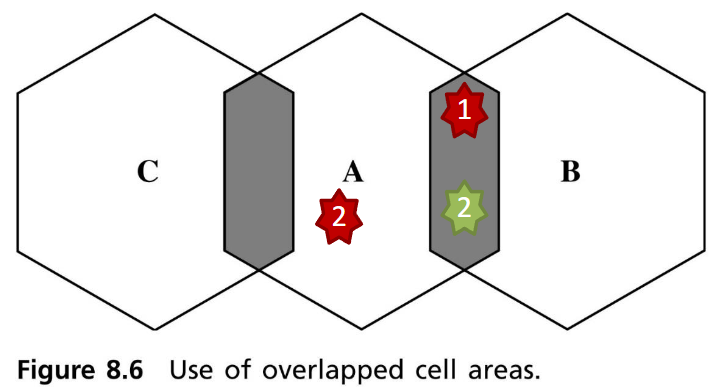
Overlapped Cells-Based Channel Allocation
不同的 cell 之間可能有重疊 (Overlapped)
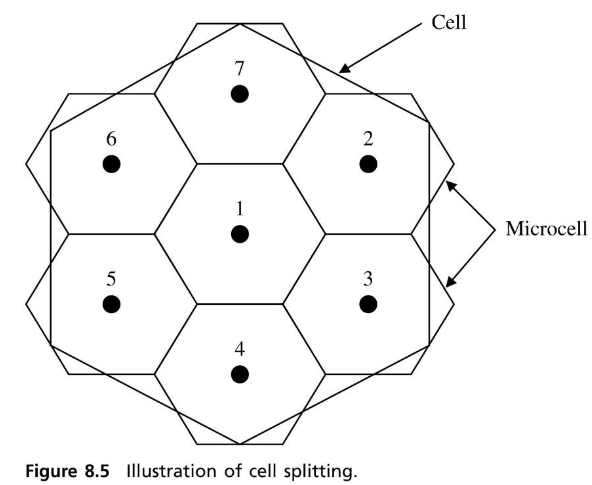
- Cell vs. microcell (覆蓋範圍較小的 cell)
- Layout 1
- Alternative one - 根據 MS 的 Mobility (移動性) 分類
Slow mobility: 由 microcell BS 分配頻道Fast mobility: 由 cell BS 分配頻道
- Alternative two - 根據 traffic 控制 microcell 開關
Low traffic: 關閉 microcell- As
traffic increases(造成資源不足或是 co-channel interference): 開啟相應的 microcell
- Alternative one - 根據 MS 的 Mobility (移動性) 分類
- Layout 2
Directed retry- MS 在 cell A 和 cell B 的重疊區域,如果 cell A 沒有空頻道,則連線至 cell B
Directed handoff- 當 cell A 的頻道都已經滿了,則把 cell A 和 cell B 的重疊區域的 MS handoff 到 cell B
Fractional Frequency Reuse (FFR)
- Kinds of interference management
- FFR
- Power control
- Smart antenna
- Motivation: 積極使用
spectrum reuse(reuse 1) 以提高系統容量並簡化無線網路規劃- reuse 1: 所有 cell 使用相同的頻段
- 分類:
- Hard FFR (strict FFR)
- Soft FFR
Hard FFR
- Cell center reuse factor: 1
- Cell edge reuse factor: Δ (ex: 3)
- Require channels in total: Δ + 1
- 中心與邊緣使用者
使用不同 spectrum
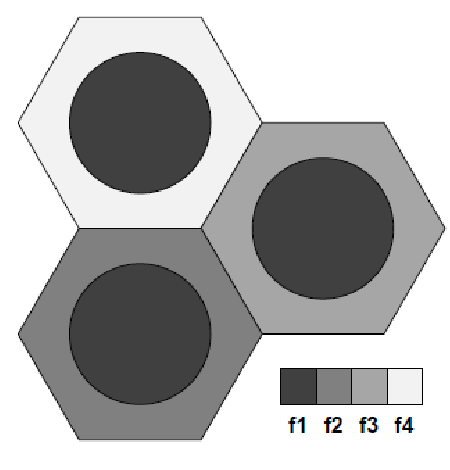
Soft FFR
- 中心與其他小區的邊緣使用者
共享部分頻譜 (sub-bands) - 中心使用
低功率,避免干擾 - 如何區分中心與邊緣使用者:
- BS-to-UE SNR
- UE location