發展心理學筆記-L11
L11 Being With Others: Forming Relationships in Young and Middle Adulthood
Relationships
Friendships
- 特徵
- based on feelings and reciprocity (互惠)
- 相較於愛情有較少的情感以及性要素
- 良好的友誼可以提高自尊
ABCDE model(友誼的各個階段)- acquaintanceship (熟人)
- buildup
- continuation
- deterioration (惡化)
- ending
- 人生階段
- 在 young adulthood 相較其他時期擁有更多的
friends and acquaintance Life transitions(ex: 結婚) 朋友會減少
- 在 young adulthood 相較其他時期擁有更多的
- Online Age
- 大量網路用戶 - 朋友增加
- online friendships:
- 需要
信任 - 也有可能像是現實的朋友那樣強的關係
- 有利於害羞的人
- 需要
- 男女差異
- 女 - 情緒分享 & 信任
- 男 - 共同活動、興趣
- 異性友誼
- Men with cross-sex friendships show lower dating anxiety and a higher capacity for intimacy
- 當有伴侶之後就很難維持
Love Relationship
- Three basic components of love:
Passion- 生理渴望Intimacy- 分享所有想法/行動Commitment- 無論好壞共同度過
- 時期
- 初期 - Passion & Intimacy 高、Commitment 低
- 後期 - Passion & Intimacy 低、Commitment 高
Finding Partne
- Assortative mating 選型婚配
- 根據彼此的相似性找到伴侶
- 教育水平、外貌吸引力 (
Physical attractiveness)、宗教…
- Dating
- Speed dating
- 短時間內與幾個人見面
- young adults
- On-line dating
- 外貌吸引力影響很大
- 第一印象由照片主導
- Speed dating
- 全球趨勢
Secure romantic attachments占大多數 (80%)Global patternsexist in mate selection and romantic relationships- 文化差異:
- based on the status hierarch (門當戶對)
- 良好的醫療保健、教育和其他資源 -> Secure romantic attachments
- 有些國家的婚姻都是被安排好的
Violence in Relationships
- Abusive relationship (虐待關係)
- 對伴侶造成侵略性的關係
Battered woman syndrome受虐婦女綜合症- 女人認為自己不能離開虐待局勢,甚至可能殺死虐待者
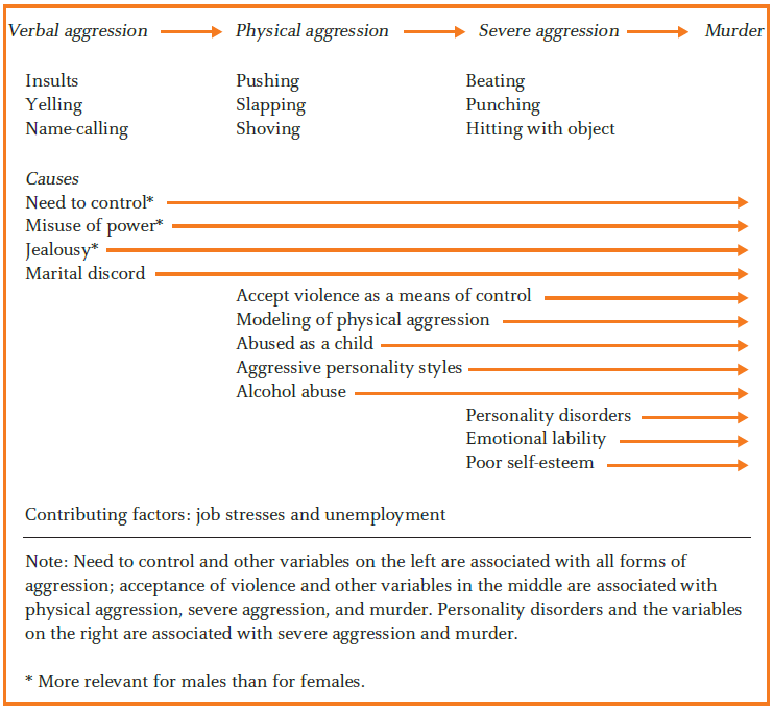
- The continuum of aggressive behaviors toward a partner:
- Verbal aggression
- Physical aggression
- Severe aggression
- Murder
- 侵略行為的根本原因隨著侵略行為的類型的變化而有所不同
Lifestyles
Singlehood
- Stereotypes - 通常對於單身人士存在很多刻板印象與偏見
- 性別差異: 女性單身者較少
- 文化、種族影響
- gradual decision (漸進決定)
- For most people, the decision to never marry is a gradual one
Cohabitation (同居)
- 伴侶關係,但是沒有結婚
- 原因:
- 結婚前的適應、測試
- 方便
- 結婚的替代
- 同居替代結婚的趨勢逐漸增加
- 全球差異: 歐洲國家較多
- 不一定會使婚姻關係較好
Gay and Lesbian Couples
- 與異性伴侶的差異:
- 雙重收入、共同負責家務
- 做出承諾、同居更快
- 彼此之間的相似程度較低
- 較少的家庭支持
- 社會對於同性戀者的態度逐漸變化
- 合法性、權利
Marriage
- About:
- Marital success: 任何婚姻結果
- Marital quality: 基於幾個不同方面的主觀度量
- Marital adjustment: 伴侶互相接納、包容的程度
- Marital satisfaction: 對婚姻的全面評估
- 預測成功的婚姻:
- 年齡 - 年紀較小的伴侶更可能離婚
- 同質 (Homogamy) - 擁有相似的價值觀與興趣更有可能持續
- 平等
Exchange theory: 婚姻關係建立在伴侶都能提供某種對方難以輕易獲得的資源、特質或價值
- happy
- Childrearing years: 快樂程度降低
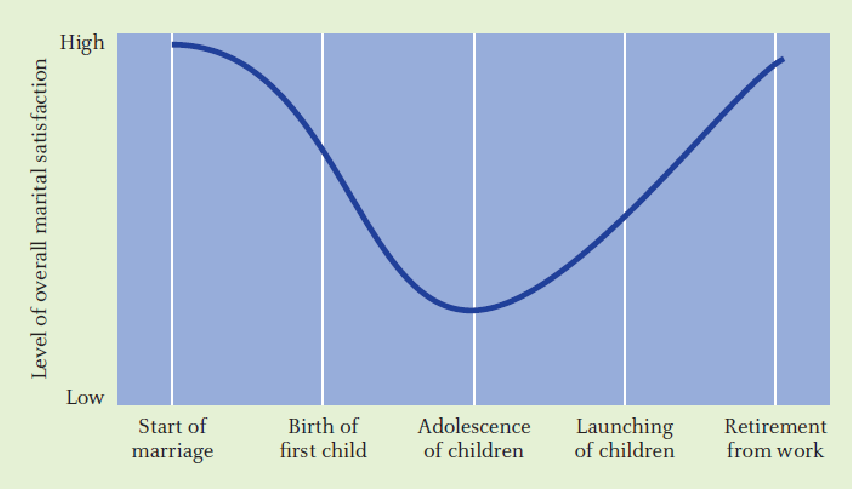
- 因素
- unequal dependence (不平等的依賴)
- 可能造成壓力與衝突
- changing patterns (模式改變)
- 能夠處理婚姻中模式的改變是長久與幸福的關鍵
- 婚姻滿意度改變
- 對婚姻中壓力和變化的反應決定伴侶是否會結婚或離婚
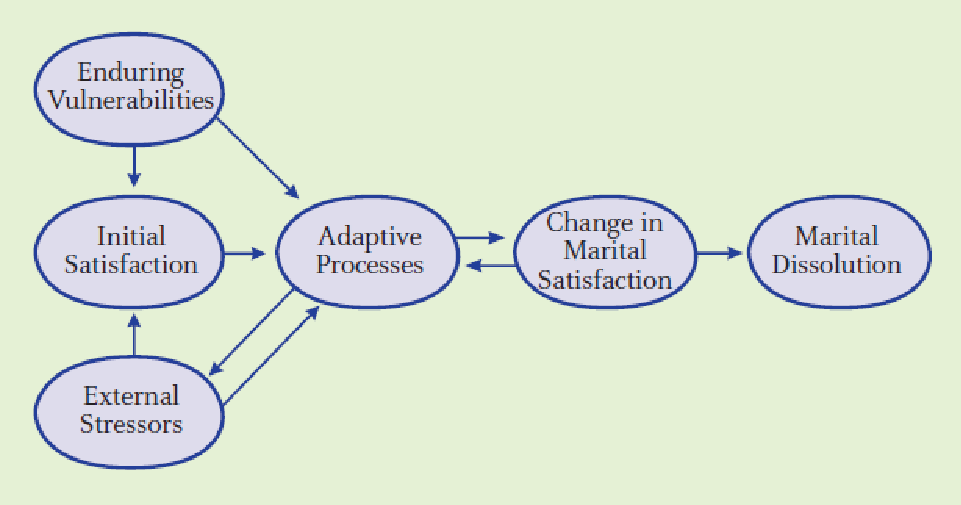
- unequal dependence (不平等的依賴)
- 如何保持幸福
- Good stress- and conflict-resistance strategies - 經歷事件後使得關係更穩固
- Romance - 保持浪漫
- Spirituality (靈性) - 分享宗教信仰和靈性
- Communication - 清處且真誠的交流想法、行動和感受
The Family Cycle
The Family Life Cycle
常見家庭類型:
Nuclear family核心家庭- 只有父母和兒童
- 常見於西方
Extended family大家庭- 父母和兒童 + 祖父母或其它親戚
Deciding Whether to Have Children
- 有孩子的好處
- 增進感情
- 改善家庭關係
- 成就感
- 傳宗接代
- 不生子的考慮因素
- 生理因素 (ex: 不孕)
- 花費
- 個人選擇
- 沒有孩子的夫妻
- 更高的婚姻滿意度
- 自由
- 更高的生活品質
The Parental Role
Multiethnic families多民族家庭- 面臨歧視與偏見
- 可能同時被兩個種族拒絕
- 母親在建立文化認同時扮演重要角色
Single parents- 父母感到沮喪或內疚
- 經濟困難
- 父母認為約會和性行為是不安全的
- Untypical parents
- 和孩子沒有基因聯繫
Stepparents- 行為和情感問題
- 讓孩子以自己的節奏接納繼父母
Adoptive parents(收養)- 孩子可能想尋求親生父母
- 與原本家庭有文化差異
Foster parents(寄養)- 因為時間限制,可能無法建立關係
- 對於發展 attachments 還是很重要
Divorce and Remarriage
Divorce
- 原因:
- 早期: 因為爭執產生的負面情緒
- 晚期: 缺乏正面情緒
Covenant marriage契約婚姻- 擴大婚姻契約內容的制度,強調雙方在社群支持下,對婚姻關係做出終身承諾
- 是一種有爭議性,避免離婚的方式
- 對父母的影響:
- 感受: 失望、拋棄
Divorce hangover- 難以適應離婚後的生活Remarrying- 中老年婦女可能難以再婚- 經濟困難
- 對孩童的影響:
- 與父母關係較差
- 之後難以建立浪漫關係
- 撫養權分配 - 沒有獲得撫養權的一方可能難以參與孩子的成長
Collaborative Divorce- 共同協商和平解決問題,避免傷害孩子
Remarriage
- 父母的角色定位不明顯 (相較於第一次婚姻)
- 男生的再婚率較高
- 女性在再婚後可能會獲得更多好處
補充 - Relationships
What Hurts Relationships?
Conflict- 衝突的數量與爭論內容不如處理方式重要
- 關鍵是如何處理衝突
- 惡性循環 (harsh setup) 導致負面互惠 (negative reciprocity)
- negative reciprocity: 一連串負面互動的循環,彼此互相傷害
- 衝突的數量與爭論內容不如處理方式重要
- Demand–Withdraw Pattern and Stonewalling
Demand–Withdraw Pattern流程:- criticism and complaining 一方的批評與抱怨
- contempt from the other 另一方感到被鄙視/輕視
- defensiveness 引發防衛心態/反擊
- withdrawal 退出對話或情感交流
Stonewalling- 當
withdrawal變得極端,某一方完全拒絕溝通,藉此懲罰對方 - 對婚姻關係非常有害
- 當
How to Nurture Positive Relationships That Last?
The Seven Principles for Making Marriage Work: (Gottman & Silver, 1999)
- Enhance your love maps - 關心並瞭解對方的內心世界和生活細節
- Nurture your fondness and admiration - 正向與樂觀看待對方,記住關係中的美好時刻
- Turn toward each other instead of away - 每天 “stop, look, and listen” 彼此
- Let your partner influence you - 分享權力與影響力,避免固執己見
- Solve your solvable problems - 衝突解決的五步驟:
- 軟化衝突的開端
- 學習修復關係
- 安撫自己和對方
- 達成妥協
- 寬容彼此的缺點
- Overcome gridlock and move toward dialogue - 承認並關心彼此的夢想
- 夢想是個人的希望、目標和渴望
- 衝突常來自夢想的差異,必須先承認並尊重差異,才能找到妥協之道
- Create shared meaning - 珍惜與重視彼此共同生活的價值
Conclusion
- Learn to love, live, and have a good life
- Keep learning and have fun discovering yourself





