通訊原理筆記-L10
L10 Existing Wireless Systems
History of Mobile Telecommunication Systems
- 1G
- 1980 年代初
- Analog communication technique (類比)
- Cell 範圍大,頻譜利用率低
- 行動裝置尺寸大
- 2G
- 1990 年代初
- Digital communication technology (數位)
- 更好的頻譜利用率,裝置價格較低
- 初始支援音訊,後來加入 short message service (SMS)
- 系統:
GSM(Global System for Mobile Communications) - 歐洲IS-95(cdma-One) - 高通所設計
- 2.5G
- 網路開始發展,有傳送資料的需求
GPRS(General Packet Radio Service) 搭配 GSMIS-95B搭配 IS-95
- 3G
- 2000 年後
- 網路需要更大的 data rates
- 系統:
UMTS(Universal Mobile Telecommunication System)- developed from GSM
- 修改 air interface 的技術 -> 與 2G 不相容 (無線部分)
cdma2000- developed from IS-95
- 4G
- 應對 Mobile Data 不斷增加
- 改變:
- Cell 範圍縮小
- 頻寬增加
- 改進通訊技術
- 降低成本
- 降低 end-to-end delay
- 提高性能
3G 中的不同系統
- UMTS - UMTS air interface has two slightly different implementations
WCDMA(Wideband Code Division Multiple Access)- Segregation of forward and reverse transmissions:
FDD - Bandwidth: 5 MHz
- Segregation of forward and reverse transmissions:
TD-SCDMA(Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access) - 中國- Segregation of forward and reverse transmissions:
TDD - Bandwidth: 1.6 MHz
- Segregation of forward and reverse transmissions:
- 不兼容 GSM
- Voice and data segregation 使用相同頻率
- cdma2000
- Bandwidth: 1.25 MHz
- 兼容 IS-95
- Voice and data segregation 使用不同頻率
Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS)
美國的第一代 (1G) 蜂巢式行動通訊系統
- Created by AT&T Bell Labs
- Speech signals: FM
- Control information: FSK
- 7 cells form a cluster
- Allow
cell sectoringandcell splitting - FDD
- Frequency band from MSs to BS: 824 MHz ~ 849 MHz
- Frequency band from BS to MSs: 869MHz ~ 894 MHz
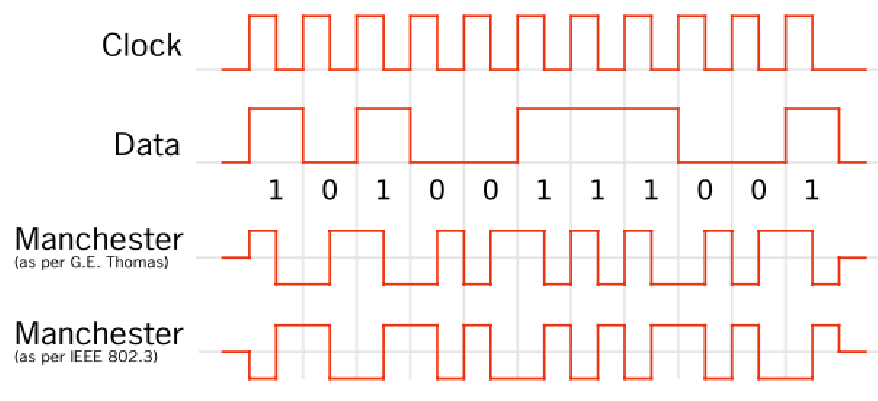
- 使用
Manchester frequency modulation在10 kbps的頻率下傳輸資料- Manchester encoding:
- 使用定向傳播避免干擾 (cell sectoring and cell splitting)
- Identification Numbers:
ESN(Electronic serial number)- 唯一識別每個 MS
- 製造商在出廠時設定
- 不可修改,每部 MS 必須具備此編號
SID(System identification number)- cellular system 的編號
- MS 在服務區域註冊時使用
- MS 要先傳送 SID 之後才能建立通話連線
MIN(Mobile identification number)- MS 的 10 位數電話號碼的數位表示
Control Channels
FOCC(Forward control channel)- BS -> MS
- 用於
Paging (尋呼)以及定位 MS Continuous data stream(連續的資料流)- Control information is through
3-way time division multiplexingmode:- Stream A: MS 的 MIN least significant bit (LSB) 為 0
- Stream B: MS 的 MIN least significant bit (LSB) 為 1
RECC busy/idle bits- 告知 MS 目前 RECC 的狀態 (是否有人使用)
RECC(Reverse control channel)- MS -> BS
Discontinuous and contention channel(不連續的競爭通道)- Discontinuous: 只在需要時才使用 RECC
- contention: 多個 MS 可能同時嘗試使用,可能發生碰撞
- 使用原因
- Paging/query response (回應)
- MSs make origination calls (主動發起通話)
- 搭配
DCC避免 co-channel interference- DCC (Digital Color Code) - 標識和區分不同的通訊群組避免干擾
Voice Channels
FVC(Forward Voice Channel)- BS -> MS
- 一對一的傳輸,且訊息量有限制
- supports two tones:
SAT(Continuous supervisory audio): 確保傳輸質量- BS 傳送資料給 MS 時加入 SAT,之後 MS 再將其回傳給 BS
- 回傳時可能加上
Signalling Tone (ST)用來確認基地台發送的命令 - BS 比對回傳的 SAT 可以檢測路徑中的 noise
- 決定是否進行 Handoff 或 Call Release
- 決定是否接受 Signalling Tone
Discontinuous data stream: 分配或調整 voice channel
RVC(Reverse Voice Channel)- MS -> BS
- 一對一傳輸
- Continuous supervisory audio tone: 偵測干擾 (SAT)
- Discontinuous data: 確認 (ST)
Initialization & Call Origination
-
Initialization:
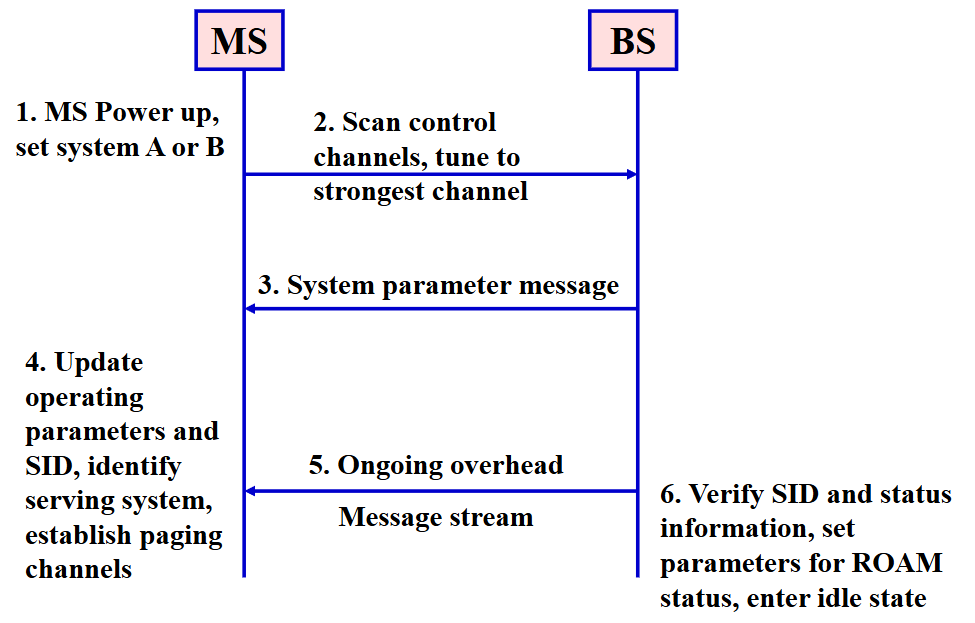
-
Call Origination:
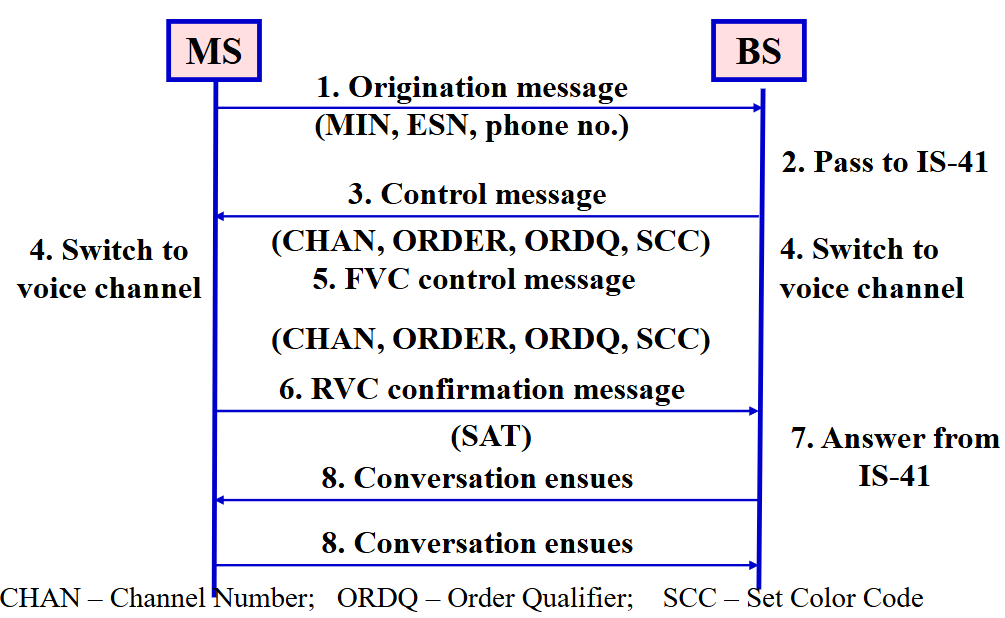
-
IS-41
- 允許在不同 MSC 控制的 BS 間進行
handoff - 允許 MS
roaming (漫遊)至 home system 以外 - defines the call origination, call delivery, and terminal registration
- Registration 過程的訊號交換對象
- 新 Serving MSC - 關聯的資料庫 (VLR)
- 新 database (VLR) - HLR
- HLR - 舊的 VLR / Serving MSC
- Registration 流程:
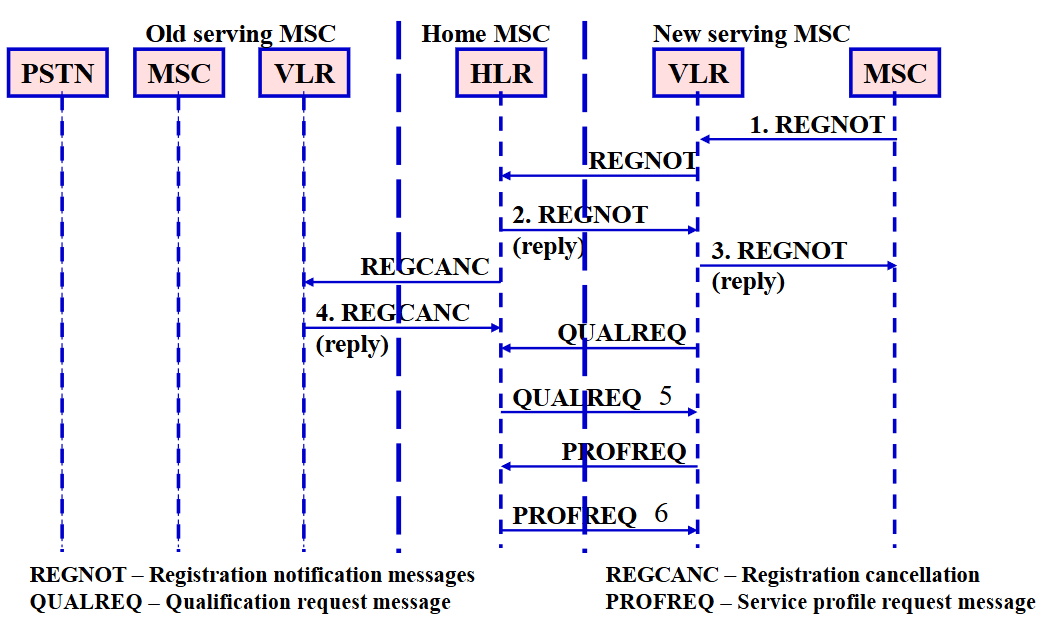
- 允許在不同 MSC 控制的 BS 間進行
-
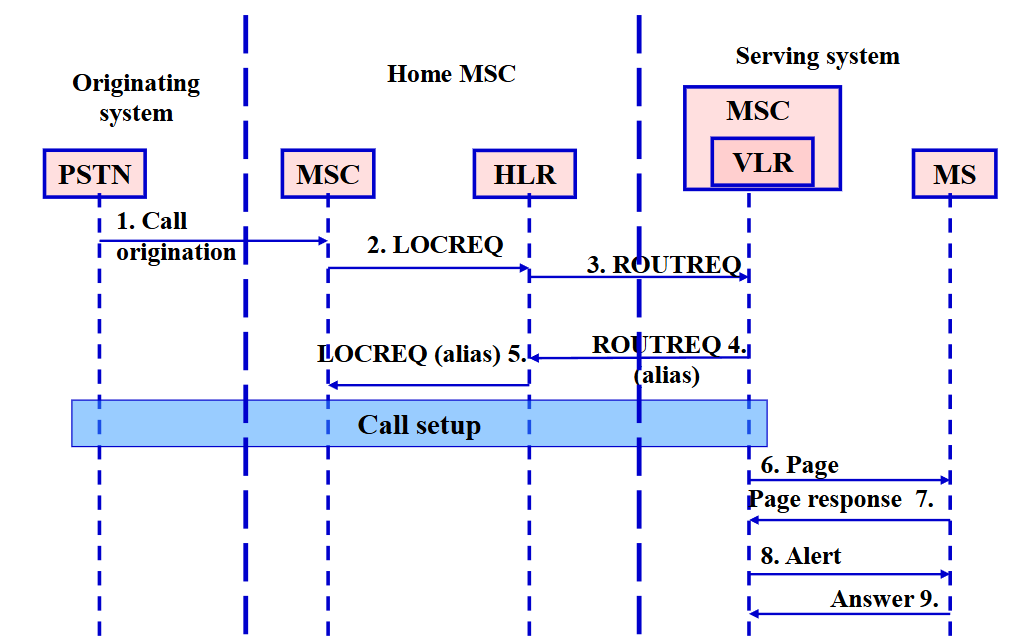
Interworking of IS-41 and AMPS
GSM
第二代(2G)行動通訊系統
- 目標: 打破各國系統不相容問題,實現全球漫遊
- 支援:
- 語音傳輸
- 數據傳輸
- 緊急通話
- Infrastructure
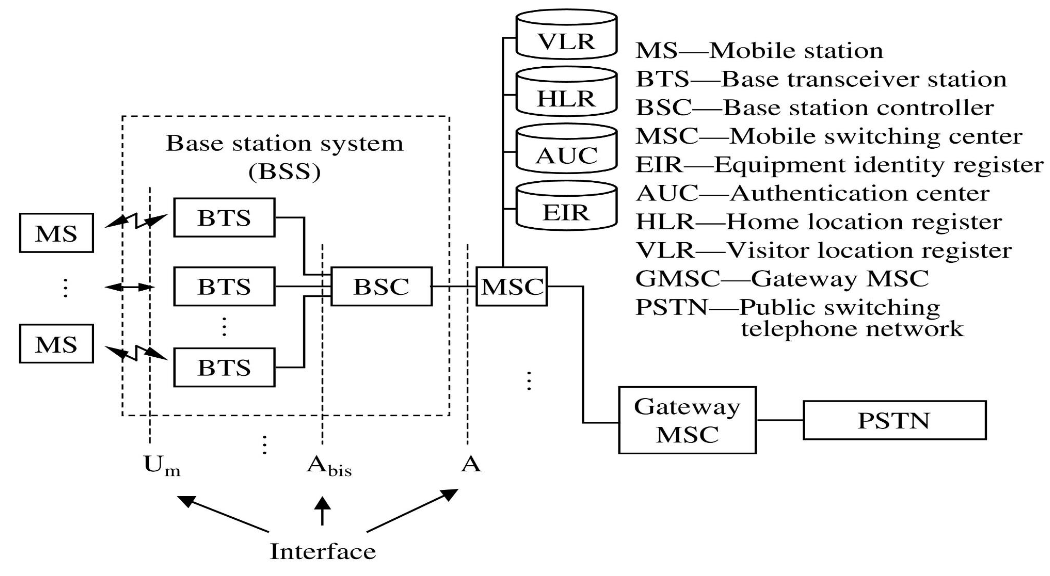
- Structure of GSM network
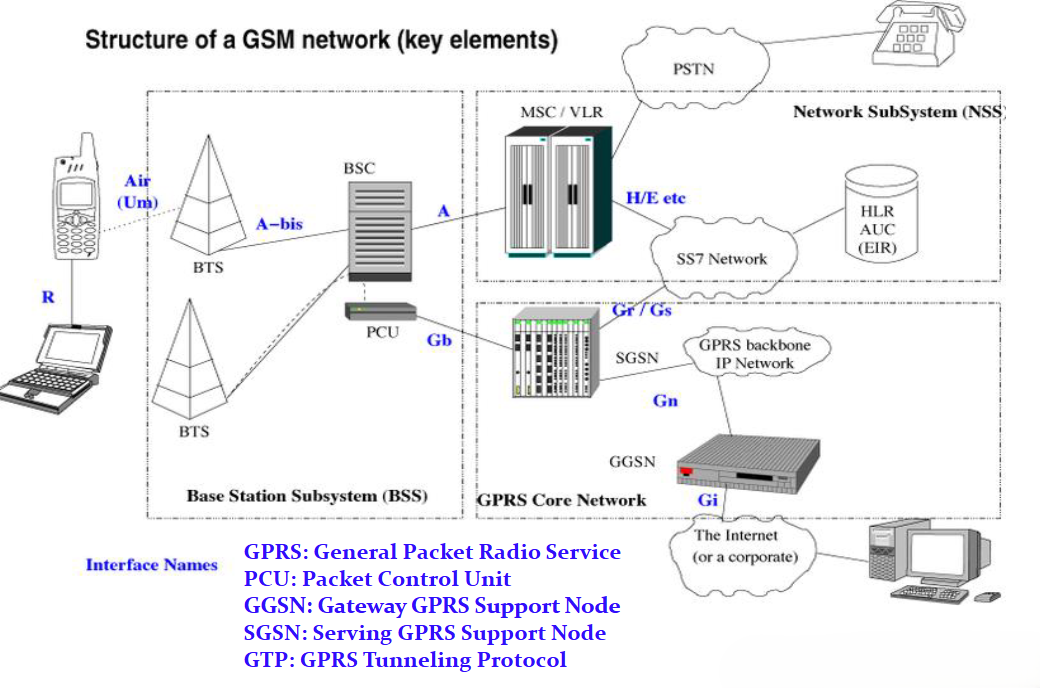
- 利用
FDMA- 最多同時服務 124 個 MS
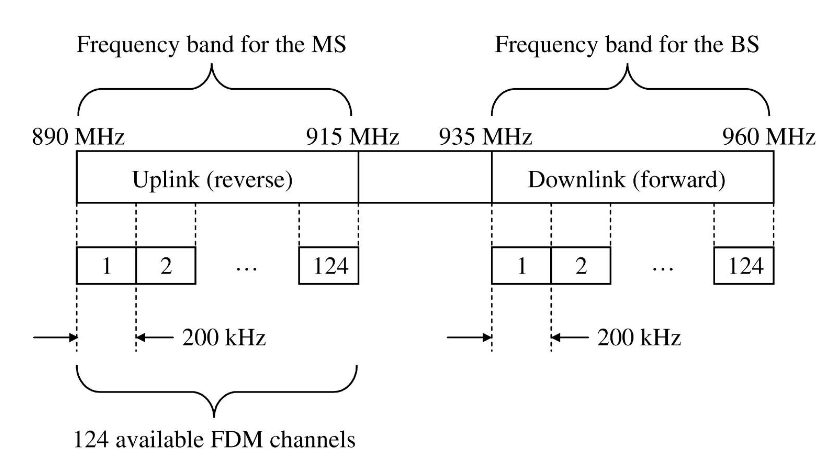
Channels
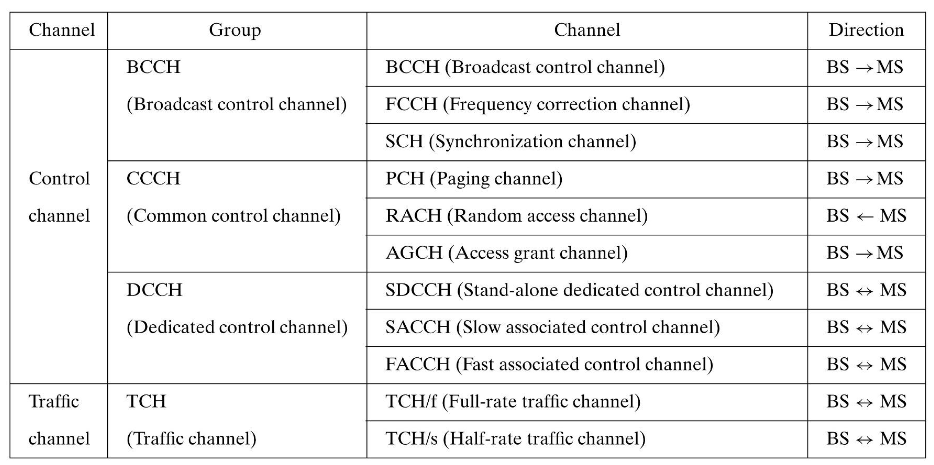
- Broadcast channels
BCCH: 廣播系統參數 (ex: frequency, operator identifier)FCCH: 提供頻率參考與校正訊號 (MS 對齊 BS 的頻率)SCH: 提供時間同步訊號 (MS 同步至 BTS 的 TDMA 架構)
- Link establishment and ongoing call management
RACH: 請求與網路建立連線 (initiates a call or responds to a page)PCH: BS 與單一 MS 通信 (BTS page MS)AGCH: 授權通道與時序資訊
- Dedicated control channels
SACCH:- 與使用者通道同時配置,用於持續傳送背景控制資訊
- BS -> MS: power control and timing information
- MS -> BS: RSSI/link quality report
SDCCH:- 與 SACCH 同時配置,負責訊號傳輸
- Call Setup
- Authentication
- Location Update
- SMS point to point use
FACCH:- 不是獨立通道,是 traffic channel 的一部分
- 傳誦與 SDCCH 相同的資料
- Channel combination:
- 頻道由
logical channels組成 - ex:
- (i) TCH/F+FACCH/F+SACCH/TF
- (ii) TCH/H(0,1)+FACCH/H (0,1)+SACCH/TH(0,1)
- (iii) TCH/H(0)+FACCH/H (0)+SACCH/TH(1)
- …
- 頻道由
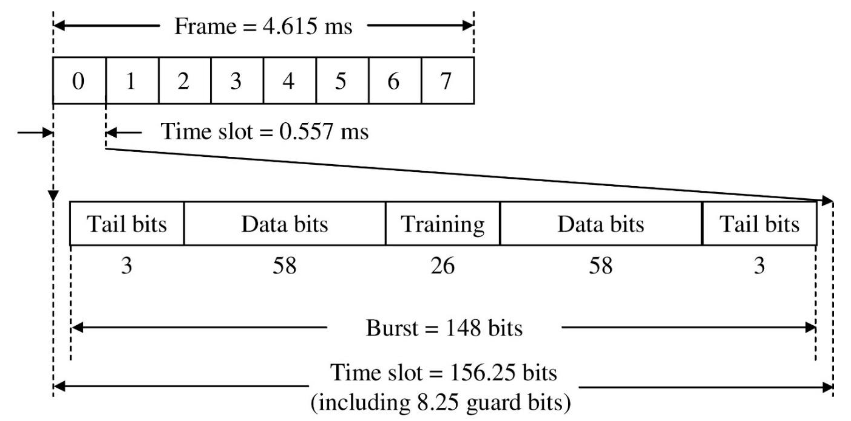
Frames
- Frames in GSM - 利用
TDMA- Frame
- Multiframe (26 frames 120ms, 24 are for traffic, 1 for SACCH)
- Superframe (51 multiframes, 6.12 sec)
- Hyperframe (2048 superframes)
Identity numbers
IMSI(International mobile subscriber identity)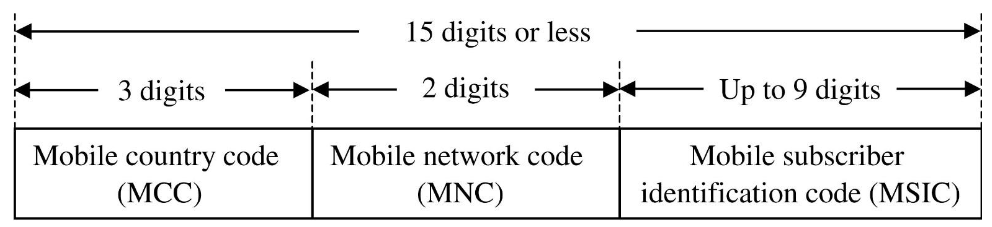
- 用來識別用戶身分
- 儲存在 SIM 卡中
- SIM (Subscriber identity module):
- 讓 MS 向 BS 表明自己的身分
- Phone number + personal identification number for the station + authentication parameters
- SIM roaming
TMSI(Temporary mobile subscriber identity)- 避免暴露用戶身份
- 當用戶連上 MSC 後,由該 MSC 的 VLR 分配
MSISDN(Mobile system ISDN)
- 電話號碼
- 用於 routing、聯絡該 MS (公開的號碼)
- MSISDN 是可以改變的 (改變門號)
LAI(Location area identity)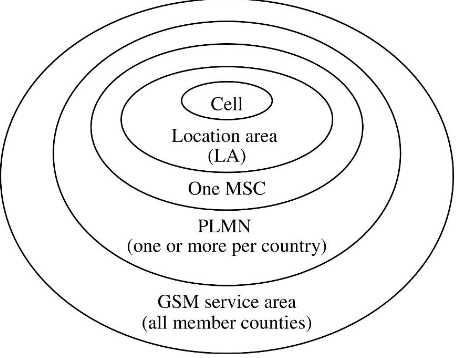
- Cells < location area (LA) < MSC < PLMN (public land mobile network)
IMSEI(International MS equipment identity)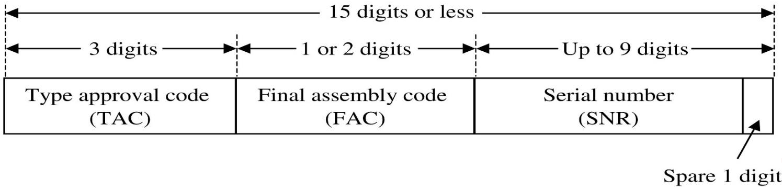
- 包含裝置的製造資訊,用來識別設備本身
- 設備通過互通性測試後,會被指派一組 TAC (type approval code)
- 設備的最終組裝地點: FAC
- 為了讓每個設備唯一,會給它一個序號 SNR
MSRN(MS roaming number )
- 用戶漫遊到另一個 MSC 時,會取得 MSRN
- 儲存在 HLR 中,讓用戶可以被呼叫
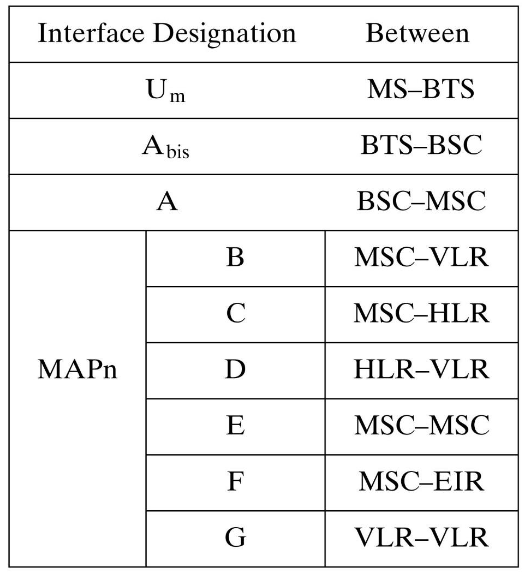
Interfaces
- Interfaces of GSM:
Functional planes
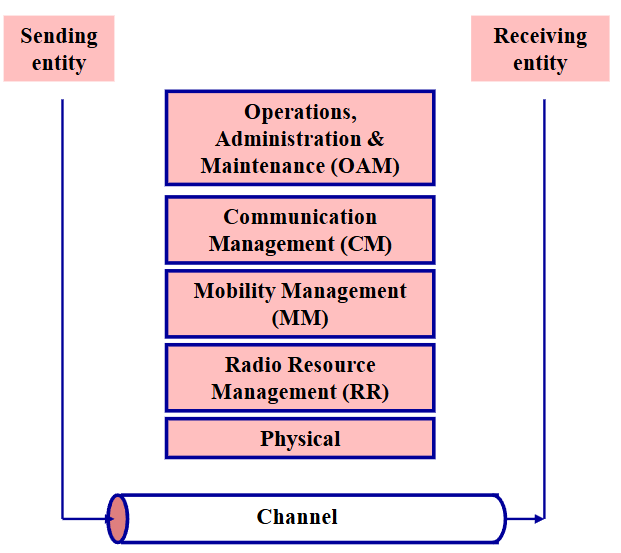
Physical plane- 傳送 user information (資料)
- 傳送 signaling messages (control signal)
Radio resource management (RR)- 負責建立、維持與釋放 MS 與 MSC 之間的通道
- 用戶移動時維持連線
- 由 MS 與 BSC 共同處理
- Static RRM
- Frequency allocation plans (NCC)
- Base station deployment
- Antenna heights
- Channel frequency plans
- Dynamic RRM
- Power control algorithms
- Precoding algorithms
- Link adaptation algorithms
- Dynamic channel allocation (DCA)
Mobility management (MM)- Security management functions
- 由 MS、HLR/AUC、MSC/VLR 共同處理
Communication management (CM)- 讓兩位用戶可以連線與對話
- 維護與釋放通話資源
- Supplementary services management (呼叫等待、轉接、來電顯示等服務)
- Short message (SMS) management
Operation, administration and maintenance (OAM)- 系統的管理後台
Others
- Authentication
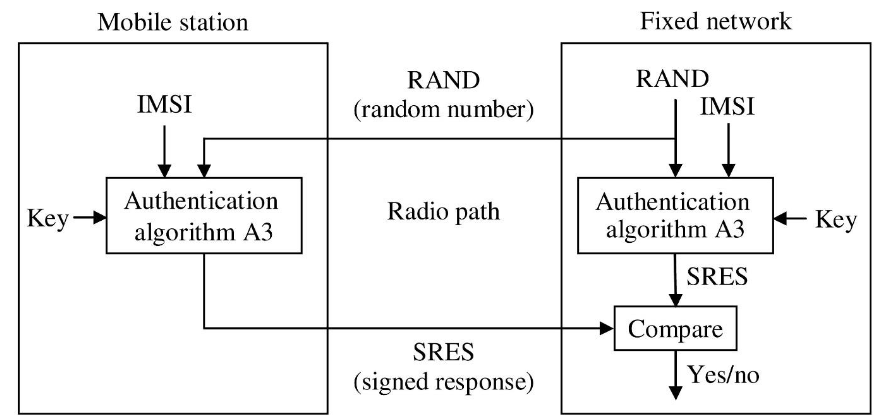
- Handoff
- Intracell/intra-BTS handoff
- 同一個 cell 內更換 time slot 或是頻率
- Intercell/intra-BSC handoff
- 同一個 BSC 內更換 cell
- MSC 參與 handoff
- Inter-BSC/intra-MSC handoff
- 同一個 MSC 內更換 BSC
- MSC 參與 handoff
- Inter-MSC handoff
- 更換 MCS
- Basic handoff: home MSC -> foreign MSC
- Subsequent handoff: foreign MSC -> foreign MSC
- Intracell/intra-BTS handoff
- Short message service (SMS)
- 在 control channels 上傳送與接收
- 傳送者可以確認簡訊是否成功送達對方手機
- 支援非文字訊息
- 不是直接寄給接收者,經由簡訊中心轉送
IMT-2000
ITU (International Telecommunications Union) 提出的第三代(3G)行動通訊標準
CDMA-basedstandard- Standardization work
- Europe: UMTS (W-CDMA)
- Japan: W-CDMA
- USA: cdma2000
- China: TD-SCDMA
UMTS
歐洲的第三代 (3G) 行動通訊標準
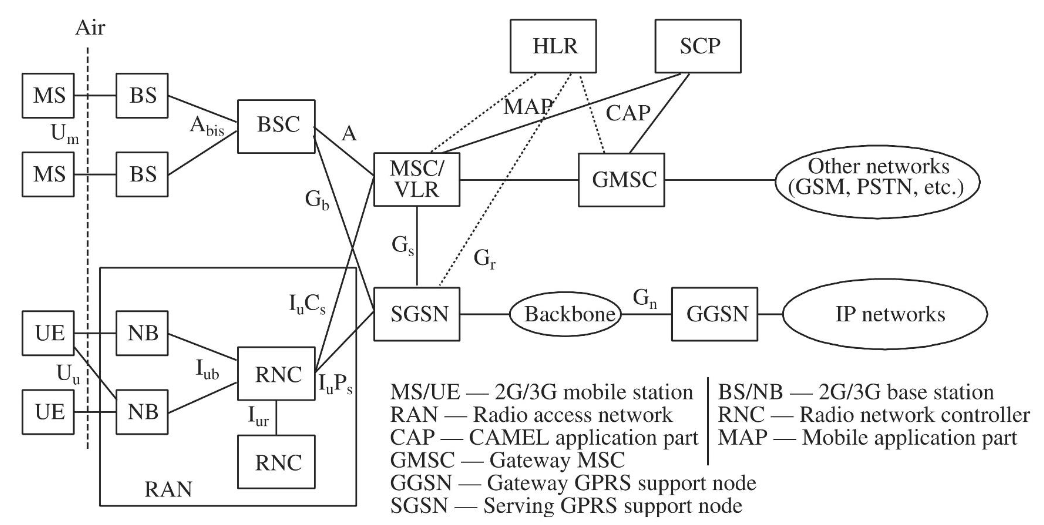
- 採用 W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access)
- 包含:
- Radio access network (
UTRAN) - Core network (Mobile Application Part, MAP)
- Authentication
- Radio access network (
UTRAN
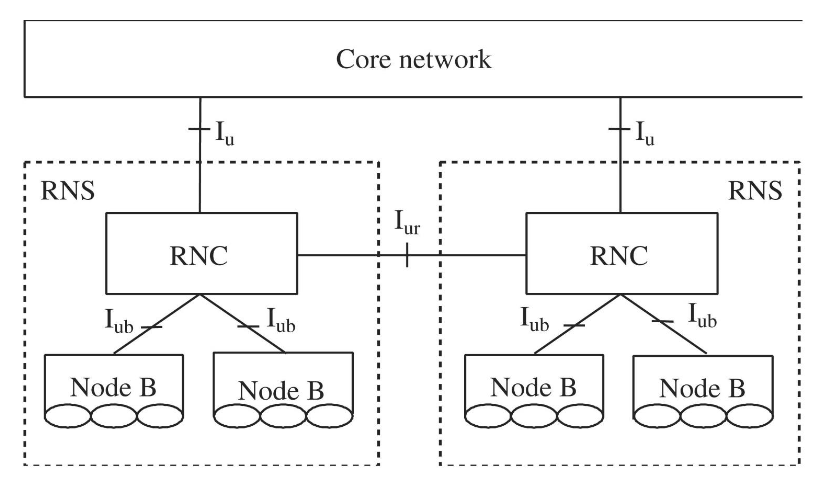
RNS: radio network subsystemsNode B(類似 BTS) - 負責訊號的發射與接收RNC(類似 BSC) - 負責管理與控制
- Protocol structure:
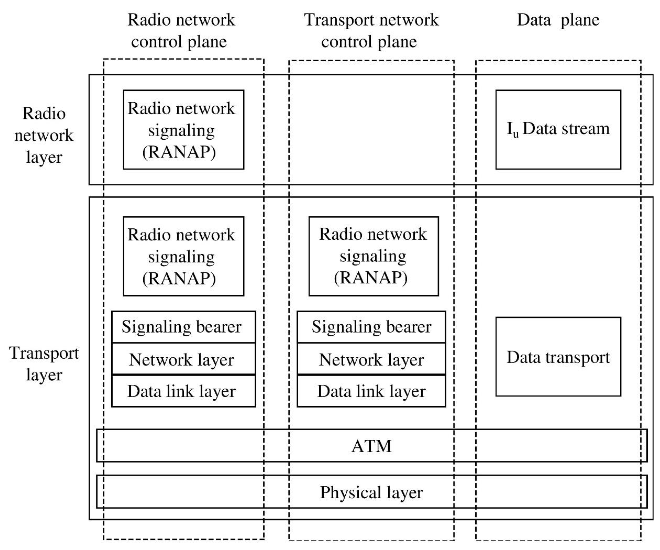
- Channels
Transport channels- 定義資料的傳送方式Logical channels- 定義資料的類型Physical channels- FDD
- carrier frequency
- access code (接取碼)
- relative phase (相位差) of the signal in the uplink
- TDD
- carrier frequency
- access code
- relative phase of the signal in the uplink
- time slot
- FDD
- Protocol stack
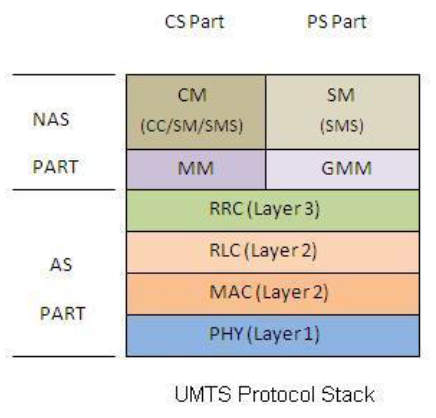
AS(Access Stratum)- 處理 UE (手機) 與無線接入網 (如 Node B, RNC) 之間的通訊
- 包含 OSI 模型的第 1 到第 3 層 (PHY, MAC, RRC)
NAS(Non Access Stratum)- UE 與核心網 (CN) 之間的訊息交換
CS(circuit switched) - 電話- CM (connection management) layers
- MM (mobility management) layers
PS(packet switched) - 網路- SM (session management) layers
- GMM (GPRS mobility management) layers
- Data plane
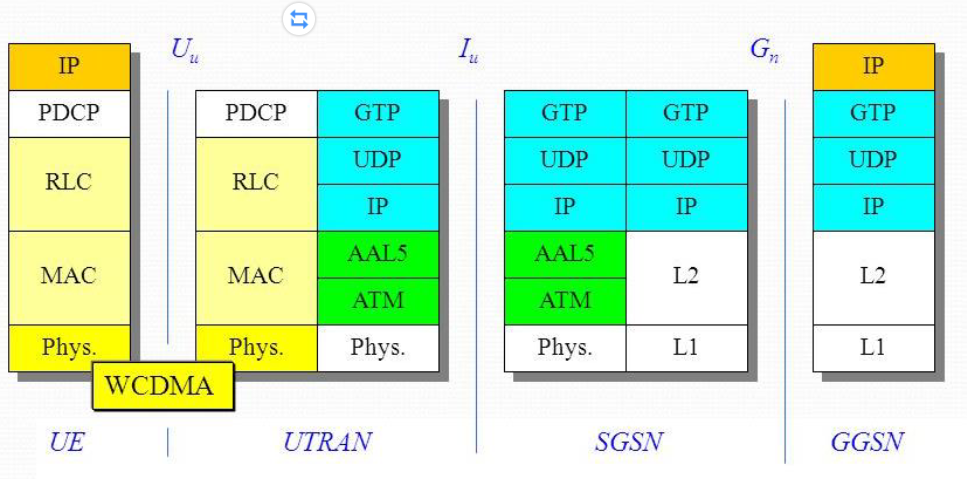
From UMTS to LTE
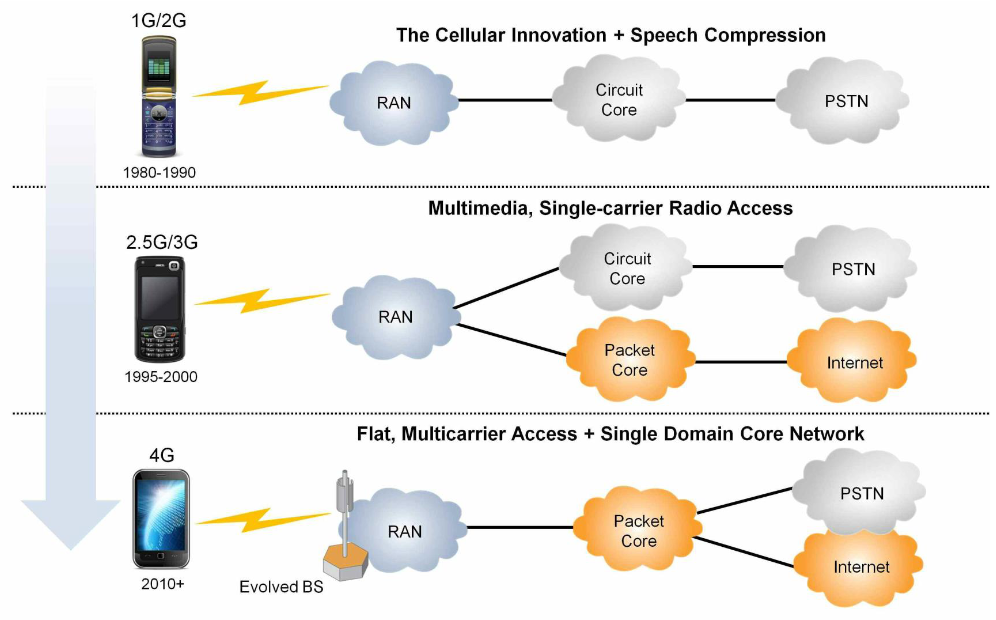
EPC(Evolved Packet Core) 替代 packet switched domain of UMTS and GSME-UTRAN(Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network) 替代 UTRAN- 處理 EPC 與行動裝置之間的無線通訊
- 3GPP working items:
SAE(System architecture evolution) - 核心網路LTE(Long term evolution) - 無線接入技術
- 完整的名稱:
EPS(Evolved Packet System)- LTE 指的只是無線技術的演進
LTE
- 4G LTE FDD & TDD
- FDD 與 TDD 是互補的技術
- 共用大部分的設計與標準
- 使用相同的核心網路
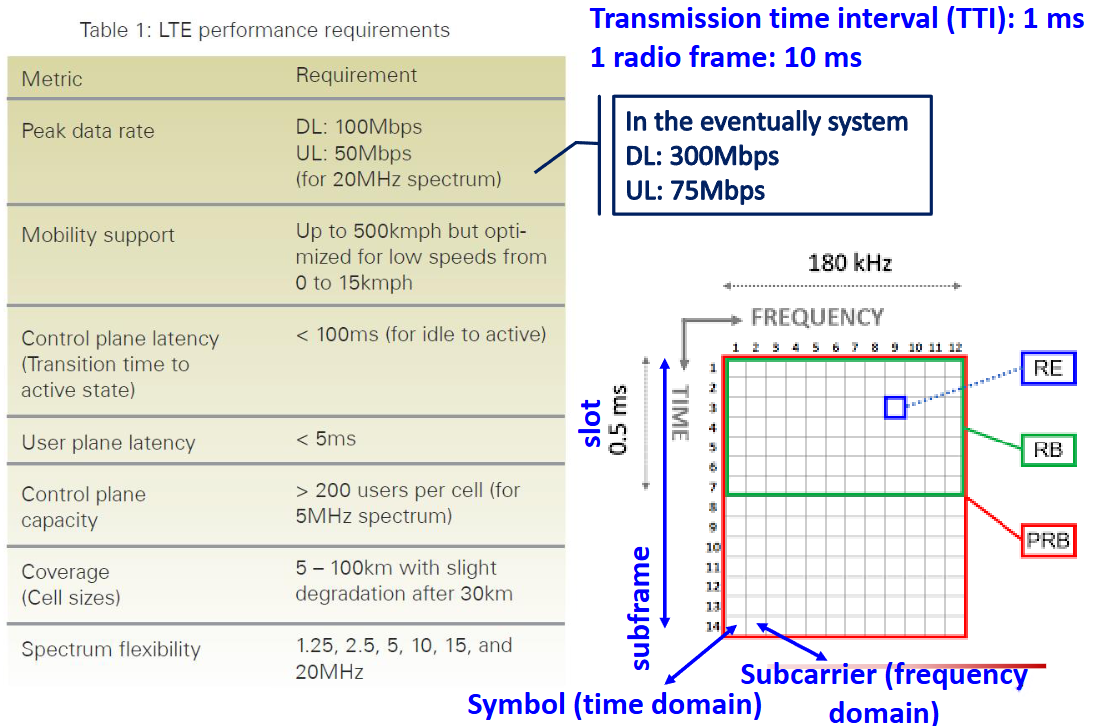
- RE (Resource Element) - 最小的資源單位
- 1 RE = 1 subcarrier × 1 OFDM symbol
- RB (Resource Block) - LTE 的基本資源配置單位
- PRB (Physical Resource Block) - RB 的具體實體分配版本

LTE Network Architecture
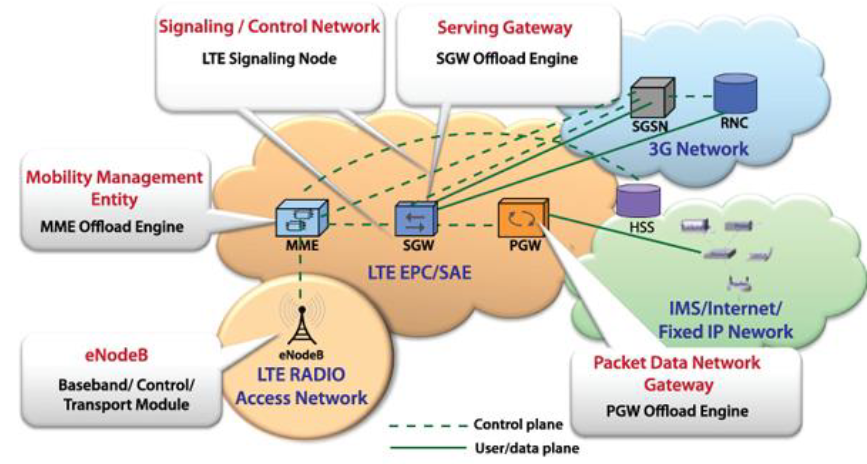
- LTE radio access network (RAN)
UE(user equipment)eNB(E-UTRAN Node B)
- LTE EPC (核心網路):
MME(mobility management entity)- 與 HSS 交互作用進行使用者認證
- 追蹤 UE 所在位置
- 行動性支援 (handover)
SGW(serving gateway)- 負責資料封包的路由與轉送
- 處理不同接入系統之間的資料轉發
- 管理與儲存 UE 的資訊 (IP Bearer 的參數、路由資訊)
PGW(PDN gateway)- 連接 UE 與外部 PDN,可以同時連接多個 PDN
- 政策控制與計費
- 封包過濾與監控
HSS(home subscriber service)- 中央數據庫儲存每位使用者的資訊
- 支援移動性管理、用戶認證與授權
- HLR 和 AUC 的整合版
5G Services
- ITU 將 5G 行動網路服務劃分為三大類,對應不同應用場景與需求
eMBB(Enhanced mobile broadband) - 高資料傳輸速率與頻寬uRLLC(Ultra-reliable and low-latency communications) - 低延遲且可靠性高mMTC(Massive machines type communications) - 大規模連接能力
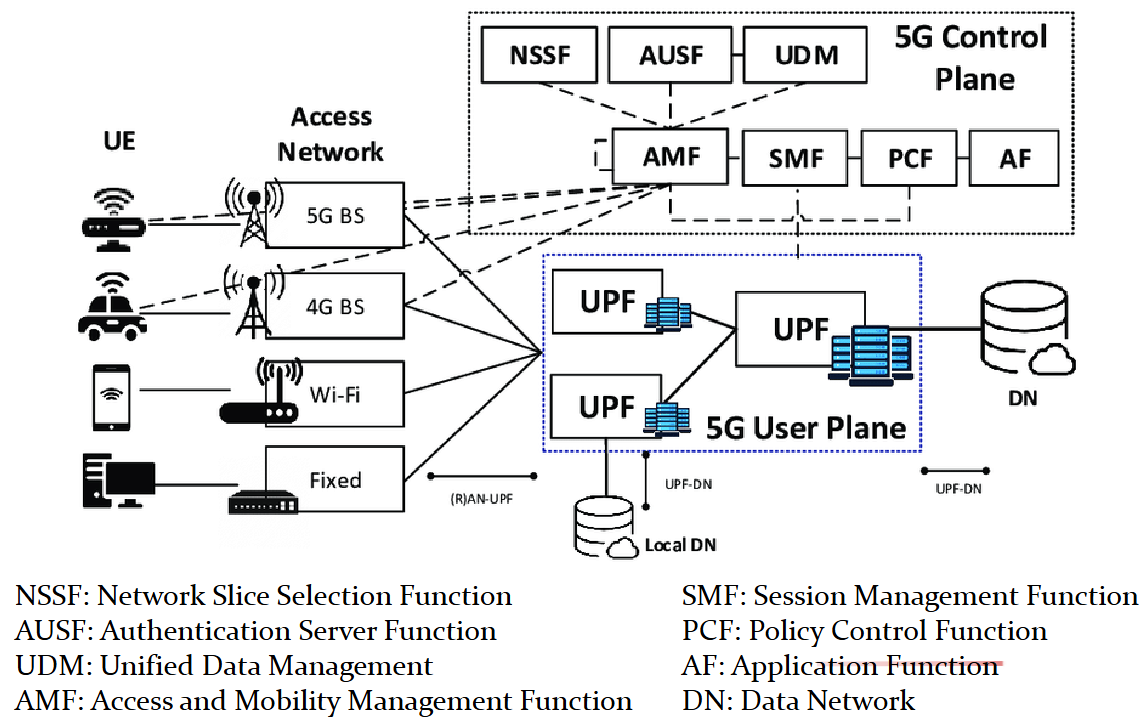
統整
結構比較
| 功能類別 | 1G | 2G (GSM) | 3G (UMTS) | 4G (LTE) | 5G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基地台 | BTS | BTS + BSC | NodeB + RNC | eNodeB (eNB) | gNodeB (gNB) |
| 無線控制元件 | 無 | BSC | RNC | eNodeB | gNB |
| 用戶位置管理 | 無 | VLR + HLR | VLR + HLR | MME + HSS | AMF + UDM |
| 認證授權中心 | 無 | AUC | AUC | HSS | AUSF |
| 移動性管理 | 無 | MSC | MSC | MME | AMF |
| 網際網路閘道 | 無 | 無 | GGSN | PGW | UPF (合併 PGW + SGW) |
| 封包轉發節點 | 無 | 無 | SGSN | SGW | UPF |
| 政策/計費控制 | 無 | 無 | 無 | PCRF | PCF |
演進
| 世代 | 相對前一代的突破 |
|---|---|
| 2G | 類比 -> 數位、支援簡訊與語音 |
| 3G | 支援網際網路、更高的傳輸速度 |
| 4G | 提升頻寬、提高性能 |
| 5G | 高速、低延遲、支援大量連結 |
Multiple Access Technology
| 世代 | 多重存取技術 | 雙工方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 1G | FDMA | FDD |
| 2G | TDMA + FDMA | FDD 為主 |
| 3G | CDMA (WCDMA) | FDD/TDD |
| 4G | OFDMA | FDD/TDD |
| 5G | OFDMA | FDD/TDD |