正規語言-L2
正規語言相關文章參考資料為陳穎平教授上課講義
L2 Context-Free Languages
Context-Free Grammars
CFGs: 上下文無關文法,指的是字元在進行替換時不需要考慮上下文,其擁有足夠的表現力來表示大多數程式設計語言的語法
Formal Definition of CFGs
DefinitionA context-free grammar is a 4-tuple , where
- is a finite set called the
variables; - is a finite set, disjoint from ,called the
terminals; - is a finite set of
rules(or productions), with each rule being a variable and a string of variables and terminals; - is the
start variable.
Each rule consists of
head:variableinsymbol →body: a string in
Ambiguity
Leftmost derivation: A derivation of a string w in a grammar G is a leftmost derivation if at every step the leftmost remaining variable is the one replaced.
A string is derived ambiguously in context-free grammar if it has two or more different leftmost derivations. Grammar is ambiguous if it generates some string ambiguously.
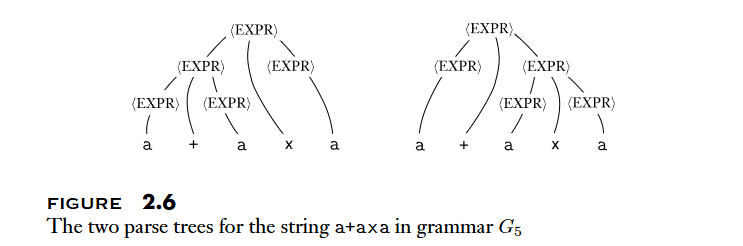
Inherently ambiguous: The context-free languages that can be generated only by ambiguous grammars. For example, .
Chomsky Normal Form
DefinitionA context-free grammar is in Chomsky normal form if every rule is of the form , where is any terminal and , , and are any variables except that and may not be the start variable. In addition we permit the rule , where is the start variable.
Any context-free language is generated by a context-free grammar in Chomsky normal form.
- 證明: Convert any context-free grammar into
Chomsky normal form:- Add a new
start variable; - Eliminate all rules ();
- Handle all unit rules ();
- Convert all rules into the proper form.
- Add a new


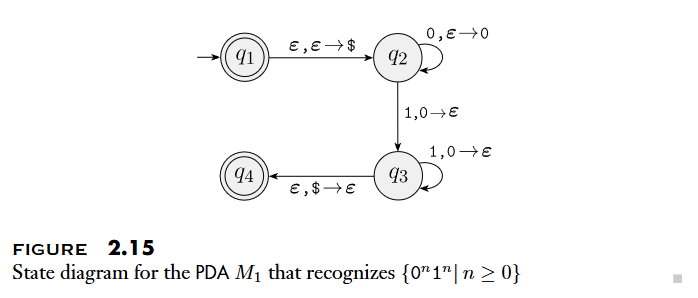
Pushdown Automata
PDA: 下推自動機
Formal Definition of PDAs
DefinitionA pushdown automaton is a 6-tuple ,where , , , and are all finite sets, and
- is the set of
states; - is the
input alphabet; - is the
stack alphabet; - : is the
transition function; - is the
start state; - is the set of
accept states.
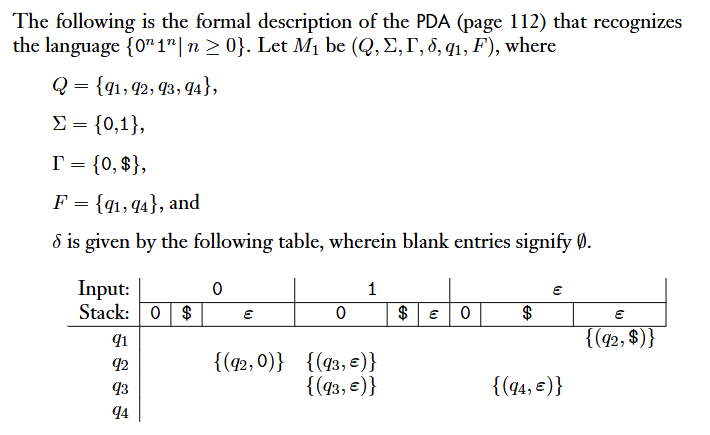
A pushdown automaton accepts input if can be written as , where and sequences of states and strings exist that satisfy the following three conditions. The stings represent the sequences of stack contents that has on the accepting branch of the computation.
- and ;
- For , we have , where and for some and ;
- .
Equivalence with CFGs
TheoremA language is context free if and only if some pushdown automaton recognizes it.
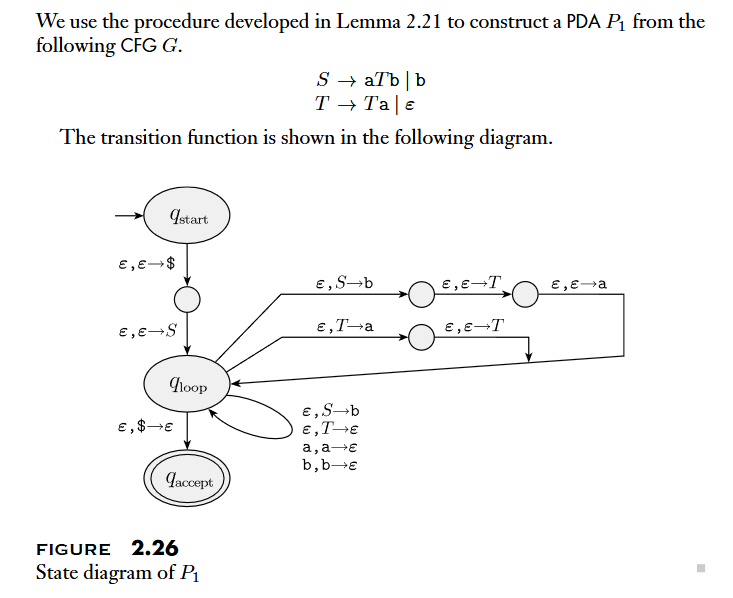
If a language is context free, then some pushdown automaton recognizes it.
- 證明: Convert the given
CFGinto aPDA.- 利用 PDA 的
nondeterminism特性,用leftmost derivation產生所有可能的 substitution sequence, 將intermediate strings儲存在 stack 中並且與 input string 進行對應,如果能到達Accept states代表能夠接受 - For the symbol on the stack top, two kinds of transitions:
- For
terminal, match the input: - For
variable, apply the rule:
- For
- 利用 PDA 的
 Lemma
Lemma
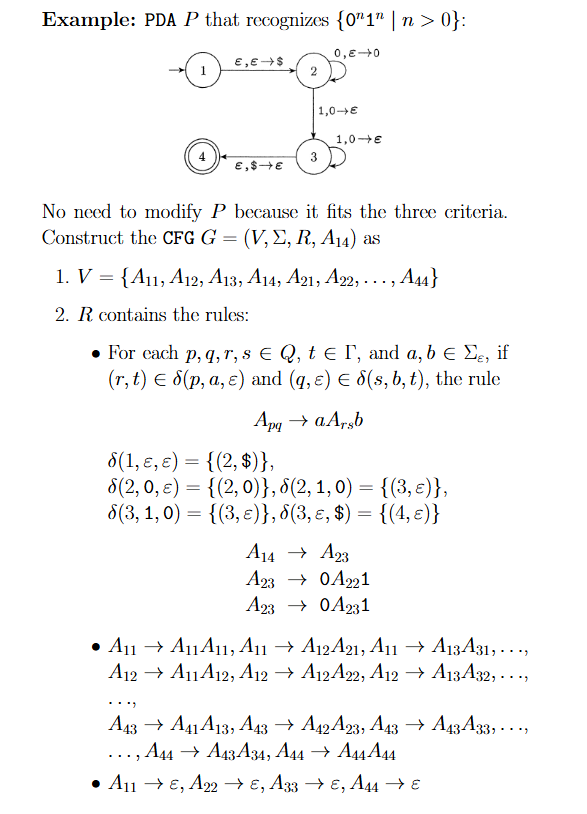
If a pushdown automaton recognizes some language, then it is context free.
- 證明: Convert the given
PDAinto an equivalentCFG.- 讓
PDA的each pair of states產生一個 代表從 到 能夠產生的所有 strings - Modify the
PDAsuch that- It has a single
accept state, .- 將原有的
accept states指向新的 ( arrow)
- 將原有的
- It empties its stack before accepting.
- 使用 符號
- Each transition either
pushes a symbolonto the stack
(a push move) orpops one offthe stack (a pop move),
but it doesnot do both at the same time.- 將 拆為
- It has a single
- For a
PDA, we construct aCFGwith the following steps:- contains the following three sets of rules:
- For each , , and , if and , the rule
- 進入到 stack 中,之後又被排出的過程
- For each , the rule
- For each , the rule
- For each , , and , if and , the rule
- 讓
 Claim
Claim
If generates , then can bring from with empty stack to with empty stack.
- 證明: Induction on the number of steps in the
derivation. (數學歸納法,從 state 轉移的角度來看)
If can bring from with empty stack to with empty stack, generates .
- 證明: Induction on the number of steps in the
computation. (數學歸納法,從 stack 的情況來看)
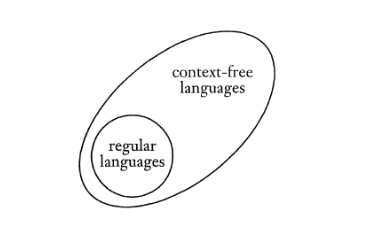
Every regular language is context free.
* NFA 可以視為 PDA 的特例
Non-Context-Free Languages
我們要如何去證明一個 Languages 是 Non-Context-Free Languages 呢?
ex: .
Pumping Lemma for CFLs
TheoremIf is a context-free language, then there is a number p (the pumping length) where, if is any string in of length at least , then may be divided into five pieces, satisfying the conditions:
- for each , ;
- ;
v, y 不同時為空字串 - .
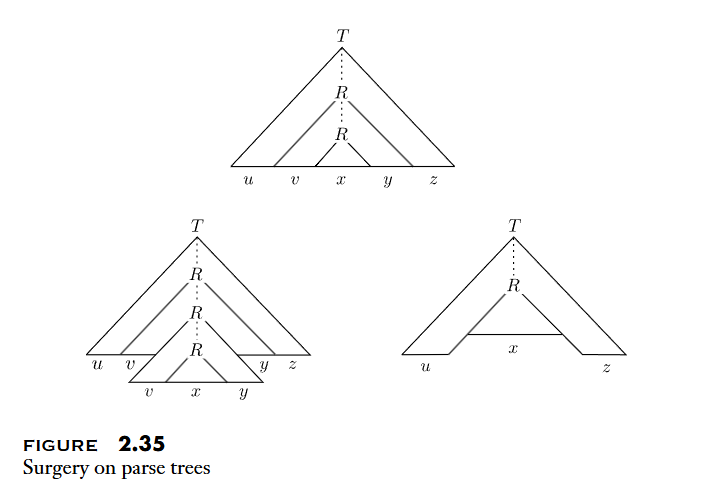
- 證明: 類似
Pumping Lemma for RL的證明方式,透過鴿籠原理,當parse tree的樹高足夠時 (> variables 總數),必定存在variable R在一條路徑中經過兩次以上,因此可以對其產生出的string進行Pumping而仍然屬於CFL
有了 Pumping Lemma for CFLs,我們可以利用反證法去證明一個 Languages 是 non-context-free languages:
- Assume the language, say, , is
context freein order to obtain a contradiction. - By the
pumping lemma for CFLs, a pumping lengthpexists, and any string can be pumped if . - Find a string , , that cannot be pumped as described in the pumping lemma.
尋找反例 - The
contradictionis obtained, and therefore, is proved to benon-context-free.

Ogden’s Lemma for CFLs
TheoremPumping Lemma for CFLs 的進階版
If is a context-free language, then there is a number p where, if is any string in of length at least , in which we select any or more positions to be distinguished, then may be divided into five pieces, satisfying the conditions:
- for each , ;
- has at least one distinguished positions;
- has at most distinguished positions.
- 如果挑選的 positions 是整個字串,就等價於
Pumping Lemma for CFLs
Example: .
- 使用
Pumping Lemma for CFLs無法證明其為non-context-free

Ogden’s Lemma for CFGs
LemmaLet be a CFG. There exists a natural number p (depending on G) such that for all , if is marked so that it has or more distinguished positions, then there exists a variable and terminal strings satisfying the following conditions:
- ;
- either or has distinguished positions;
- has no more than distinguished positions;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- for each , .
5 + 6
Inherently Ambiguous CFLs
證明 是 Inherently Ambiguous,所有能夠產生它的 grammer 都是 Ambiguous 的
- 透過
Ogden’s Lemma for CFGs,可以證明不論用什麼CFG產生 ,其中的 必定存在兩種不同的parse trees,代表該CFG是Ambiguous,故 為Inherently Ambiguous
Deterministic Context-Free Languages
[skip]
Properties of CFLs
Substitutions
is a generalization of the homomorphism we defined
in the study of regular languages
- Homomorphism:
- Substitutions:
- 一個 symbol 可以對應到多個 string
- can be extended in for strings and languages:
-
If is a CFL over , is a substitution on such that is a CFL for each , then is also a CFL.
- 證明:
- Let be the
CFGfor and be theCFGfor , for each symbol . Construct a new grammar for :- is the union of and all the ’s for .
- is the union of all the ’s for .
- consists of
- All rules in each ;
- The rule in but with each
terminal ain their
bodies replaced by everywhereaoccurs.
- 將原有的
parse trees後面接上 的parse trees
- Let be the
Closure Properties
Let and be context-free languages. Let be a regular language. The results of the following operations are all context-free languages:
Substition: ;Union: ;- 證明: 加上
Concatenation: ;- 證明: 加上
Star: ;- 證明: 加上
Reversal: ;- 證明: 將所有 rules 的 body 部分顛倒
Homomorphism: ;- 證明: Substition 的特例
Inverse homomorphism: ;- †
Intersection: ;- 不一定是
context-free languages - 證明: 類似合併兩
DFA的方式,將 的PDA和 的DFA合併
- 不一定是
- †
Difference: ().
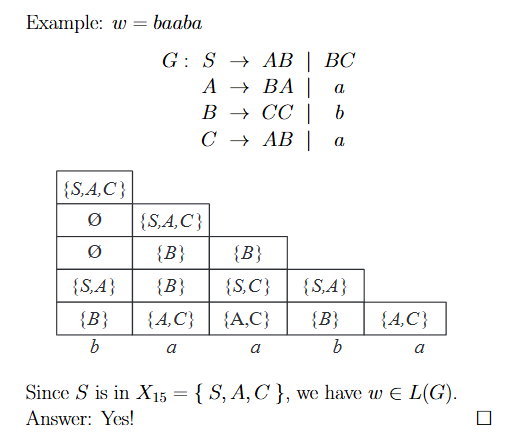
Membership Test: CYK Algorithm
檢測
- Let is the
context-free grammarfor inChomsky normal form. - The input string is of length .
- Construct the table with horizontal axis () being the positions of the symbols in , is the set of variables such that . We ask whether (i.e., .)
- Basis: is the set of variables such that can be found in the rule.
- Induction step: contains if we can find variables and , and integer such that
- ;
- is in ;
- is in ;
- is a rule.
- 由下往上填滿,最後檢查 有沒有在最上面的格子中
- 也能夠檢查 的子串列是否也屬於 (對應的格子中是否有 )