正規語言-L3
正規語言相關文章參考資料為陳穎平教授上課講義
L3 The Church-Turing Thesis
Turing Machines
圖靈機的想法: Finite control + unlimited and unrestricted memory.
- 在磁帶上面讀 & 寫
- 可以將讀取頭向左/右移動
- 磁帶是無限長的
- 可以立刻決定拒絕 (Reject) 或接受 (Accept)
Formal Definition of A Turing Machine
DefinitionA Turing machine is a 7-tuple , where are all finite sets and
- is the set of
states; - is the
input alphabetnot containing theblank symbol; - is the
tape alphabet, where and ;- 是因為需要把 input string 放到磁帶上
- 代表空的位置
- : is the
transition function;- 用於控制磁帶頭左/右移
- is the
start state; - is the
accept state; - is the
reject state.

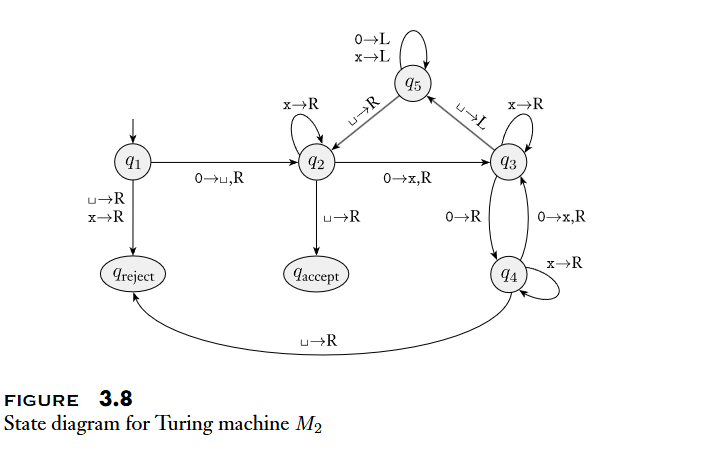
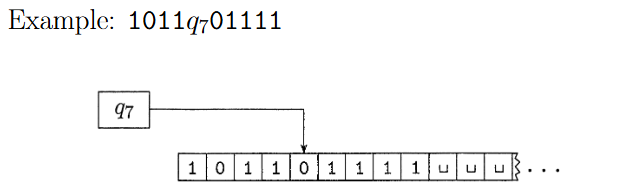
A configuration of the Turing machine consists of
- the current
state; - the current
tape contents; - the current
head location.
and is represented as for a state , two strings and over the tape alphabet , and the current head at the first symbol of .
If the Turing machine can legally go from configuration to configuration , we say that yields .
Formally, if , , and , and are two configurations.
-
yieldsif . -
yieldsif .
A Turing machine accepts input if a sequence of configurations exists, where
- is the start configuration of on input ;
- Each
yields; - is an accepting configuration.
The collection of strings that accepts is the language of , or the language recognized by , denoted .
Call a language Turing-recognizable if some Turing machine recognizes it. (Also known as recursively enumerable language)
Call a language Turing-decidable or simply decidable if some Turing machine decides it. (Also known as recursive language)
Variants of Turing Machines
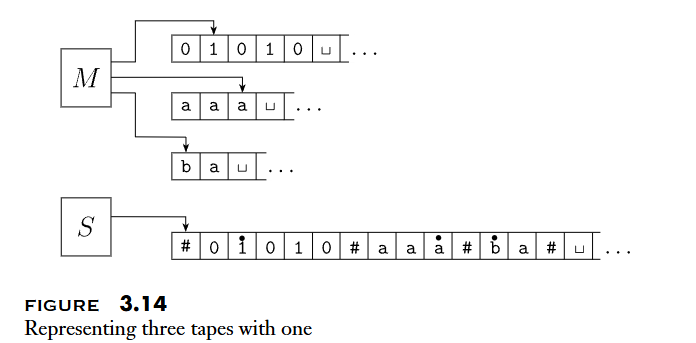
Multitape Turing Machines
k-tape Turing machine:
- : .
- 有
k個磁帶可以操作 - 每個磁帶頭可以選擇向左/右或是不動
Every multitape Turing machine has an equivalent single-tape Turing machine.
single-tape Turing machine可以視為multitape Turing machine的特例:- 可以使用
single-tape Turing machine來模擬multitape Turing machine的行為- 用 符號分隔每個
tape的資料 - 使用
dotted tape symbols代表該磁帶的磁帶頭所在位置 - 每次掃過每個
tape並記錄磁帶頭位置,透過transition function模擬行為,並對對應的tape進行操作
- 用 符號分隔每個
 Corollary
Corollary
A language is Turing-recognizable if and only if some multitape Turing machine recognizes it.
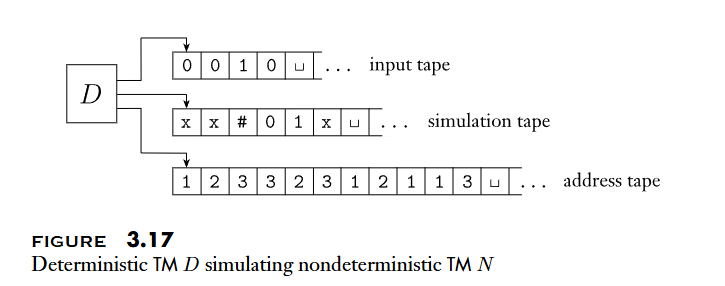
Nondeterministic Turing Machines
Nondeterministic - several choices at any point:
- : .
transition function改為 Power set
Every nondeterministic Turing machine has an equivalent deterministic Turing machine.
deterministic Turing machine可以視為nondeterministic Turing machine的特例- 把
deterministic Turing machine當作一個 queue 使用,用來儲存nondeterministic Turing machine的狀態- 用 符號分隔每個狀態
- 類似 BFS 遍歷
nondeterministic Turing machine的所有可能
 Corollary
Corollary
A language is Turing-recognizable if and only if some nondeterministic Turing machine recognizes it.
A language is decidable if and only if some nondeterministic Turing machine decides it.
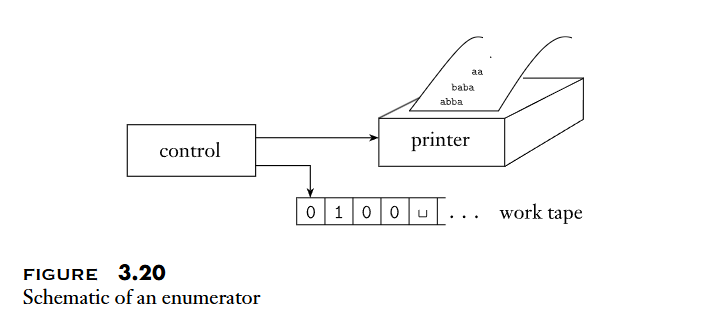
Enumerators
枚舉器: 枚舉所有字串
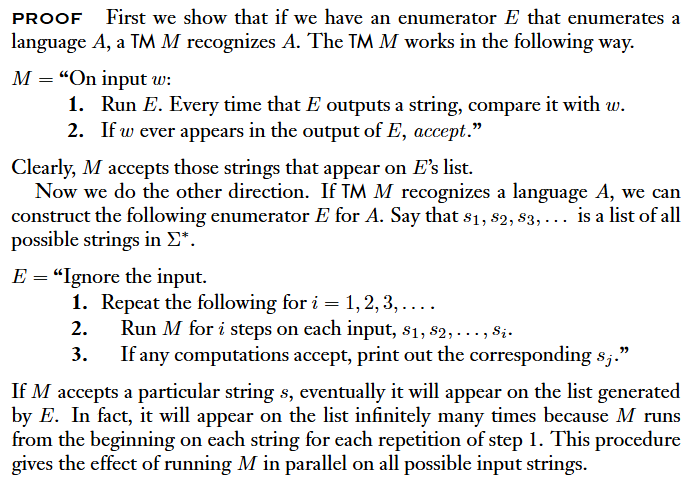
 Theorem
Theorem
A language is Turing-recognizable if and only if some enumerator enumerates it.
The Definition of Algorithm
Hilbert’s Problems
Find an algorithm to determine whether a given polynomial Diophantine equation with integer coefficients has an integer solution.
- 如何定義
algorithm?- Church: λ-calculus;
- Turing: Turing machines.
Terminology for Describing Turing Machines
The different levels of detail:
formal description: Spells out in full the Turing machine’s states, transition function, and so on;- 可以想像成 machine code/assembly code
implementation description: Describes the way that the Turing machine moves its head and the way that it stores data on its tape;- 可以想像成 C/Java code
high-level description: Describes an algorithm.- 可以想像成 pseudo code