正規語言-L7
正規語言相關文章參考資料為陳穎平教授上課講義
L7 Time Complexity
Measuring Complexity
DefinitionLet be a deterministic Turing machine that halts on all inputs. The running time or time complexity of is the function , where is the maximum number of steps that uses on any input of length . If is the running time of , we say that runs in time and that is an time Turing machine. Customarily we use to represent the length of the input.
- In
worst-case analysis, we consider the longest running time of all inputs of a particular length. - In
average-case analysis, we consider the average of all the running times of inputs of a particular length.
Big-O and Small-O Notation
In asymptotic analysis (漸進分析), we seek to understand the running time of the algorithm when it is run on large inputs: Considering the highest order term.
Let and be functions . Say that if positive integers and exist such that for every integer , .
When we say that is an upper bound for , or more precisely, that is an asymptotic upper bound for , to emphasize that we are suppressing constant factors.
Polynomial bounds: for some .Exponential bounds: for some .
Let and be functions . Say that if
In other words, means that, for any real number , a number exists, where for all . 沒有等號
Analyzing Algorithms
DefinitionLet be a function. Define the time complexity class, TIME(t(n)), to be the collection of all languages that are decidable by an time Turing machine.
- A
single-tape TMfor :

- A
single-tape TMfor :

- A
two-tape TMfor :- :
linear time
- :

Complexity Relationships among Models
The time complexity relationships for the three models:
- the single-tape Turing machine;
- the multitape Turing machine;
- the nondeterministic Turing machine.
Let be a function , where . Then every time multitape Turing machine has an equivalent time single-tape Turing machine.
- 證明: 可以用
single-tape Turing machine來模擬multitape Turing machine,每次multitape Turing machine的操作在模擬的TM上需要 的時間,故相乘之後需要 的時間 - 僅考慮 的情況,因為如果不是 的話,代表輸出結果不需要遍歷整個 input string,這個情況過於簡單,不需考慮
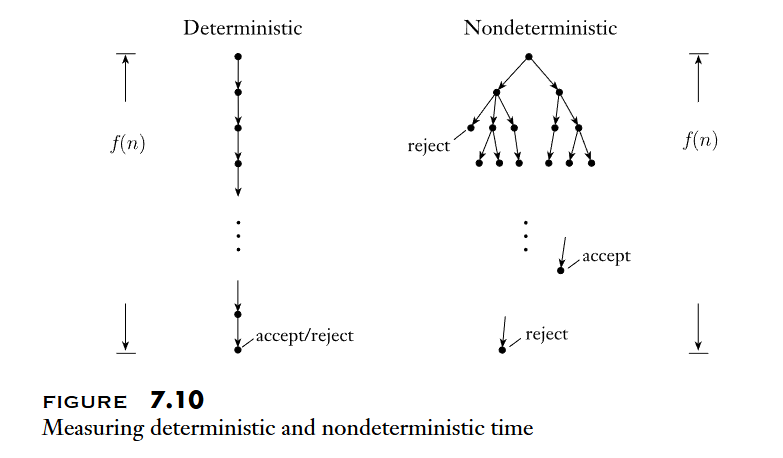
Let be a nondeterministic Turing machine that is a decider. The running time of is the function , where is the maximum number of steps that uses on any branch of its computation on any input of length .
Let be a function , where . Then every time nondeterministic single-tape Turing machine has an equivalent time deterministic single-tape Turing machine.
- 證明: 可以用
deterministic single-tape Turing machine來模擬nondeterministic single-tape Turing machine,把它當作一個 queue 來 BFS 遍歷所有可能性,假設每個 state 最多有 個可能性,則會有 種可能需要遍歷 (等比級數),而每次操作需要 的時間,故總共要 的時間
The Class P
- Single-tape TM vs. Multitape TM: At most a
polynomialdifference. - Deterministic TM vs. Nondeterministic TM: At most an
exponentialdifference.
Polynomial Time
Polynomial differences in running time are considered to be small, whereas exponential differences are considered to be large.
All reasonable deterministic computational models are polynomially equivalent. We focus on aspects of time complexity theory that are unaffected by polynomial differences in running time.
is the class of languages that are decidable in polynomial time on a deterministic single-tape Turing machine. In other words,
- Invariant for all polynomially equivalent models.
使用的 moodel 不會影響是否屬於 P - Corresponding to realistically solvable problems.
理論上 solvable
Examples of Problems in P
Describe algorithms with numbered stages for analysis:
- A
polynomialupper bound on thenumber of stages. - The individual stages can be
run in polynomial time.
Have to use reasonable encoding methods, such as base notation for any for integers. (至少使用 2 進位來表示數字)
定義
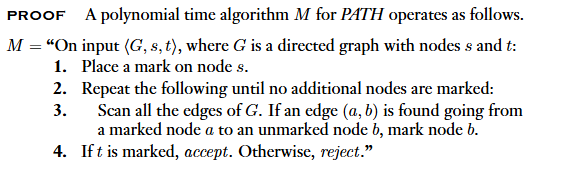
Theorem
- 證明: Use a
graph-searching method.- number of stages: 1(1) + m(3) + 1(4)
- time of individual stages:
polynomial time
定義
Theorem
- 證明: Use the
Euclidean algorithm. (輾轉相除法)- 中的每次操作至少會使 變為原本的一半,故 stage 2,3 總時間會小於 ,因為計算時間複雜度時比較的對象是
tape input 長度(假設為 2 進位),故整體為polynomial (liner) time
- 中的每次操作至少會使 變為原本的一半,故 stage 2,3 總時間會小於 ,因為計算時間複雜度時比較的對象是

Theorem
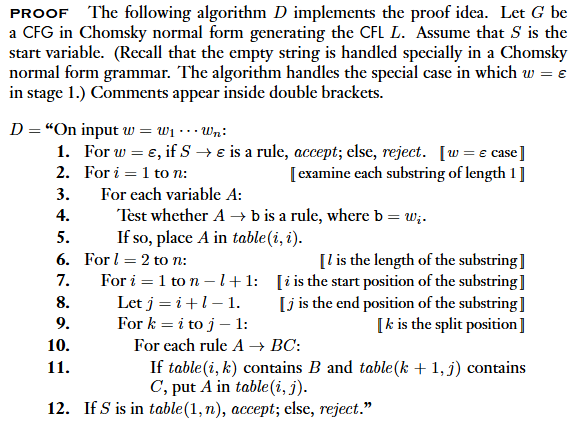
Every context-free language is a member of .
- 證明: Use the
CYK algorithm.CYK需要填入 個格子,每次填入需要檢查 種組合,共 的時間,為polynomial time
The Class NP
定義
- Hamiltonian path: 經過所有 node
定義
以上兩者都有 polynomial verifiability 的特性,可以在 polynomial time 驗證給定 certificate 是否正確。
A verifier for language is an algorithm , where .
We measure the time of a verifier only in terms of the length of , so a polynomial time verifier runs on polynomial time in the length of . A language is polynomially verifiable if it has a polynomial time verifier. is called a certificate or proof .
NP is the class of languages that have polynomial time verifiers. The term NP comes from nondeterministic polynomial time.
A language is in NP iff it is decided by some nondeterministic polynomial time Turing machine.
- 證明: Convert a
polynomial time verifierto an equivalentpolynomial time NTMand vice versa.
.
Corollary
Examples of Problems in NP
定義
- k-clique: 大小為 k 的團 (團內每個點彼此互相連接)
- 證明: The
cliqueis the certificate.

定義
- Note that and are considered
multisets. (同一元素可以出現多次)
- 證明: The
subsetis the certificate.

The P versus NP Question
- = the class of languages for which membership can be
decidedquickly. - = the class of languages for which membership can be
verifiedquickly.
目前不知道是以下哪一種情況:
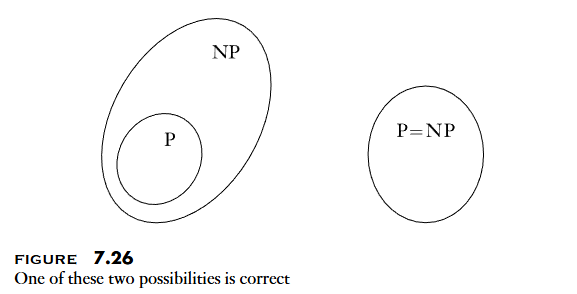
For now, we can prove that , but we don’t know whether NP is contained in a smaller deterministic time complexity class.
NP-completeness
NP-complete problem: satisfiability problem.
.
Polynomial Time Reducibility
DefinitionA function is a polynomial time computable function if some polynomial time Turing machine exists that halts with just on its tape, when started on any input .
computable function加上polynomial time的限制
Language is polynomial time mapping reducible, or simply polynomial time reducible, to language , written , if a polynomial time computable function exists, where for every , $w ∈ A ⇔ f (w) ∈ B $.
The function is called the polynomial time reduction of to .
mapping reducible加上polynomial time的限制
If and , then .
- 證明: 假設 的
polynomial time algorithm存在,則可以利用 以及polynomial time computable function建立 的polynomial time algorithm

定義:
- Literal:
- Clause:
Conjunctive normal form, cnf-formula:3cnf-formula:
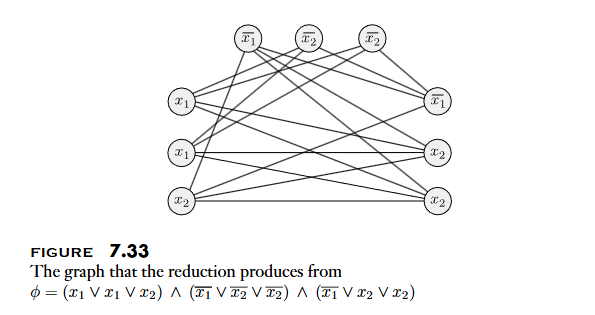
Theorem
is polynomial time reducible to .
- 證明:
- 將每個 Clause 內的 Literal 當成一個 node
- 將所有 node 互相連接,除了:
- 同個 Clause 內的 Literal
- 互為相反的 Literal ()
- 如果存在大小為 k (Clause 個數) 的團,則代表
satisfiable
Definition of NP-completeness
DefinitionA language B is NP-complete if it satisfies two conditions:
- B is in NP;
- every A in NP is polynomial time reducible to B.
If is NP-complete and , then .
- 證明: This theorem follows directly from the definition of polynomial time reducibility.
If is NP-complete and for in NP, then is NP-complete.
- 證明: Polynomial time reducible to B, then to C.
The Cook-Levin Theorem
Theoremis NP-complete.
- 證明:
- 先證明 is in NP
- 接著證明所有 A in NP is polynomial time reducible to
- 用
Boolean formula表示 的NTM的computation history是否合法- 檢查 symbol (每個格子只能有一個 symbol 為 true)
- 檢查起始狀態
- 檢查狀態轉移
- 檢查結束狀態
- 如果
computation history合法,則該Boolean formula是satisfiable - 得到
polynomial time reductionof to
- 用
 Theorem
Theorem
is NP-complete.
- 證明:
- 可以將之前的
Boolean formula轉為3cnf-formula
- 可以將之前的
Additional NP-complete Problems
Corollaryis NP-complete.
- 證明: 已知
- is polynomial time reducible to .
定義
k-node vertex cover代表只要選擇 個 node,將其所有相鄰邊塗黑,可以塗黑所有邊
is NP-complete.
- 證明: Reduce to .
- 將所有正反 variable 當成 node 置於上方
- 將每個 Clause 內的 Literal 當成一個 node 置於下方,並將 Clause 內的 node 互相連接
- 將上方的 Literal 與下方的相同 Literal 連接
- 如果這個圖為
k-node vertex cover則代表satisfiable -
- 為
Variable 個數: cover 上方的邊 & 為 true 的 Literal- 正反 variable 至少要有一個塗黑
- 為
Clause 個數: cover 為 false 的 Literal- 至少兩個 node 塗黑才能 cover 整個 Clause
- 為
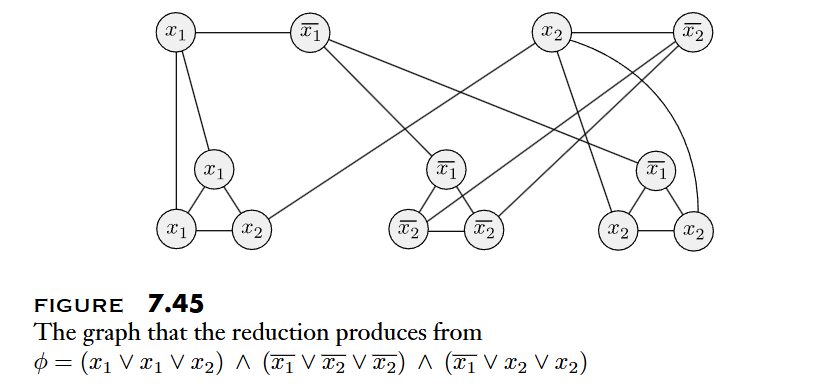
The Hamiltonian Path Problem
Theoremis NP-complete.
- 證明: Reduce to .
- 將每個 Variable 化為一個菱形圖
- 左邊為 true,右邊為 fasle
- 中間 node 總數為
- 為包含該 Variable 的 Clause 數量
- 將每個 Clause 化作一個 node
- 連接 Clause 與剛剛的菱形圖
- 正反 Variable 的方向要相反
- 連接 Clause 與剛剛的菱形圖
- 這個圖存在 Hamiltonian path 從 s 到 t,則代表
satisfiable
- 將每個 Variable 化為一個菱形圖
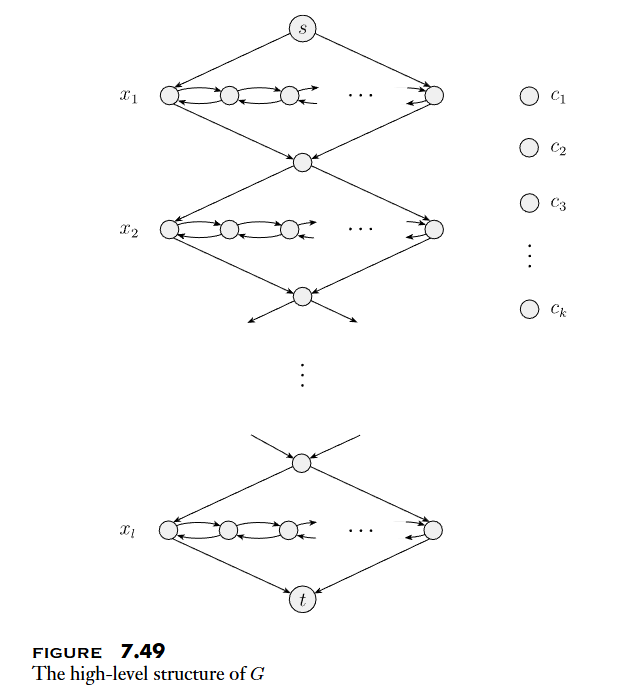
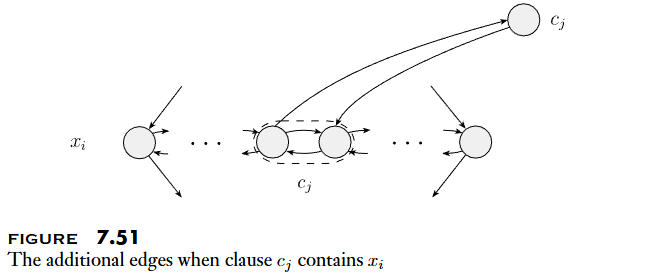
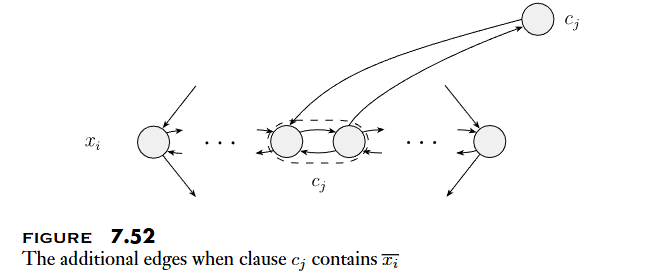
Theorem
is NP-complete.
- 證明: Reduce to .
- 把原本 HAMPATH 中的每個 node 分解 (除了 )
- 把 node 變為
- 三個 node 相連 ()
- 原有的路徑 變為
- 把原本 HAMPATH 中的每個 node 分解 (除了 )
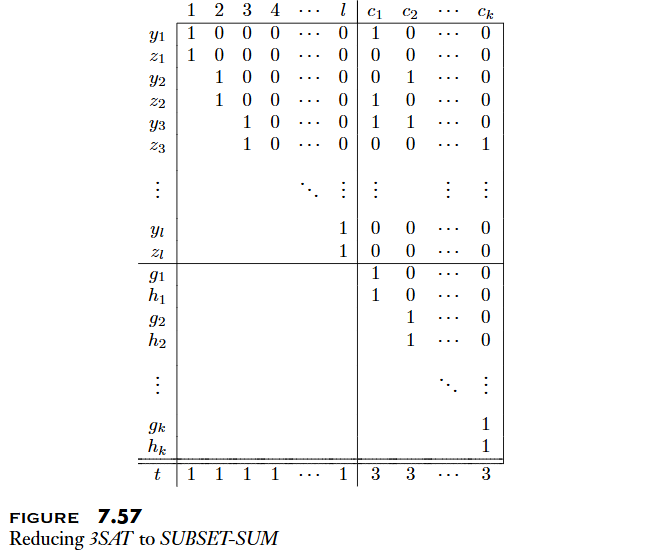
The Subset Sum Problem
Theoremis NP-complete.
- 證明: Reduce to .
- 化成一個表格
- 大小為 ()
- 為 Variable 數量
- 為 Clause 數量
- 左下角留空
- 左上和右下填法相同
- 右上角根據 Clause 與 Variable 對應填入
- 大小為 ()
- 表格的上方會決定 Variable 選擇正反
- 左邊總和為 1: 每個 Variable 不是正就是反
- 右半總和為 1~3: Clause 內至少一個為 true
- 表格的下方會把右半部分全部補成 3
- 化成一個表格